Subject:physics
Physics Form OneIntroduction to Physics
Science in our lives
Scientists are people trained in science and who practice the knowledge of science.
We require people in industries to work as engineers, technicians, researchers, in hospitals as doctors, nurses and technologists.
Science gives us powerful ideas, instruments and methods which affect us in our daily lives.
Scientific methods
1. A laboratory is a building specifically designed for scientific work and may contain many pieces of apparatus and materials for use.
2. A hypothesis is a scientific fact or statement that has not been proven or experimented.
3. A law or principle is a scientific fact or statement that has been proven and experimented to be true for all conditions.
4. A theorem is a fact or statement that is true and proven but applicable under specific conditions.
What is physics?
Physics is a Greek word meaning nature hence it deals with natural phenomena.
Physics is therefore a science whose objective is the study of components of matter and their mutual interactions.
Physics is also defined as the study of matter and its relation to energy.
A physicist is able to explain bulk properties of matter as well as other phenomena observed.
Branches of physics
1. Mechanics – the study of motion of bodies under the influence of force.
2. Electricity – this deals with the movement of charge from one point to another through a conductor.
3. Magnetism – the study of magnets and magnetic fields and their extensive applications.
4. Thermodynamics / heat – this is the study of the transformation of heat from one form to another.
5. Optics –the study of light as it travels from one media to another.
6. Waves – the study of disturbances which travel through mediums or a vacuum.
7. Particle physics
8. Nuclear physics
9. Plasma physics
Relation of physics to other subjects
Since physics enables us to understand basic components of matter and their mutual interactions it forms the base of natural science.
Biology and chemistry borrow from physics in explaining processes occurring in living things and organisms.
Physics also provides techniques which are applied almost every area of pure and applied science i.e.
meteorology, astronomy etc.
Career opportunities in physics
1 Engineering – civil
3. Surveying
4. Geology
5. Astronomy
NOTE: - all science based careers i.e. doctors, nurses, technologists, engineers, pharmacists etc. need physics as a true foundation.
Basic laboratory safety rules
1. Proper dressing must be observed, no loose clothing, hair and closed shoes must be worn.
2. Identify the location of electricity switches, fire-fighting equipment, first aid kit, gas and water supply systems.
3. Keep all windows open whenever working in the laboratory.
4. Follow all instructions carefully and never attempt anything in doubt.
5. No eating or drinking allowed in the laboratory.
6. Ensure that all electrical switches, gas and water taps are turned off when not in use.
7. Keep floors and working surfaces dry. Any spilla ge must be wiped off immediately.
8. All apparatus must be cleaned and returned in the correct location of storage after use.
9. Hands must be washed before leaving the laboratory.
10. Any accidents must be reported to the teacher immediately.
Chapter Two
Measurement
In order to measure we need to know or define the quantity to be measured and the units for measuring it.
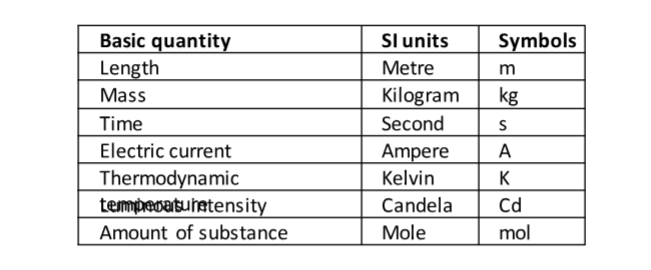
In 1971 a system known as the International System of Units (Systeme’ Internationale) and seven basic units were agreed upon as follows. Other quantities can be obtained from these basic quantities and are referred to as derived quantities.
LengthThis is the measure of distance between two points in space. The SI unit for length is the metre (m).Therefore 1 km = 1000 m
1 Hm = 100 m
1 Dm= 10 m
1 mm = 0.001 m
Length is measured using a metre rule (100 cm), tape measure (100 m, 300 m, 500 m)
Area
This is the measure of the extent of a surface. It is a derived quantity of length. Its SI units are square metres (m2). Other units are cm2, km2, etc.
Formulas are used to determine areas of regular bodies while for irregular bodies an approximation of area is used.
Volume
This is the amount of space occupied by matter. The SI units for volume is cubic metre (m3). Other sub-multiples are cm3, mm3 and l.
Hence 1 m3 = 1,000,000 cm3 and 1l= 1,000 cm3. Volume can be measured using a measuring cylinder, eureka can, pipette, burette, volumetric flask, beaker, etc.
Mass
This is the quantity of matter contained in a substance . Matter is anything that occupies space and has weight. The SI unit for mass is the Kilogram (kg).
Other sub-multiples used are grams (g), milligrams (mg) and tonnes (t). 1 kg = 1,000 g = 1,000,000 mg=100 tonnes. A beam balance is used to measure mass.
Density
This is mass per unit volume of a substance. It is symbolized by rho (ρ) and its SI units are kg/m3.
Density = mass / volume.
Examples
1. A block of glass of mass 187.5 g is 5.0 cm long, 2.0 cm thick and 7.5 cm high. Calculate the density of the glass in kgm -3.
Solution
Density = mass / volume = (187.5 /1000) /(2.0 × 7.5 × 5.0 /1,000,000) = 2,500 kgm-3.
2. The density of concentrated sulphuric acid is 1.8 g/cm 3. Calculate the volume of 3.1 kg of the acid.
Solution
Volume = mass / density = 3,100 / 1.8 = 1,722 cm3 or 0.001722 m3.
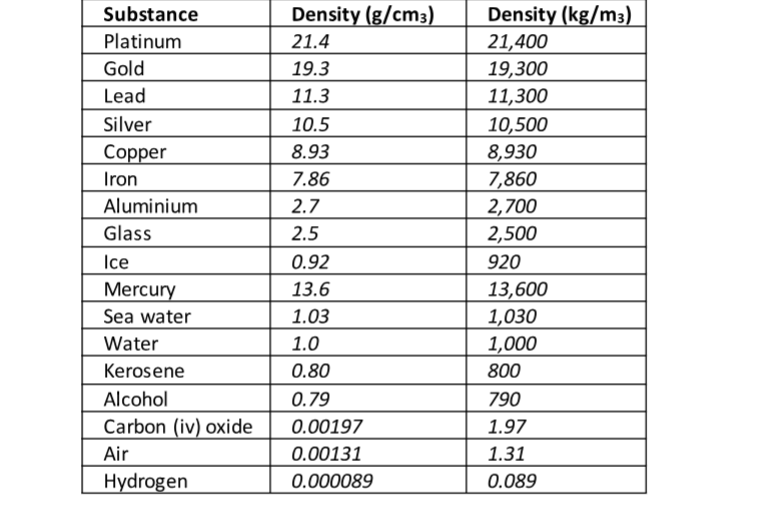
The following is a list of dens ities of some common substances
ExampleThe mass of an empty density bottle is 20 g. Its mass when filled with water is 40.0 g an d 50.0 g when filled with liquid X. Calculate the density of liquid X if the density of water is 1,000 kgm-3.
Solution
Mass of water = 40 – 20 = 20 g = 0.02 kg.
Volume of water = 0.02 / 1,000 = 0.00002 m3. Volume of liquid = volume of bottle
Mass of liquid = 50 – 20 = 30 g = 0.03 kg
Therefore density of liquid = 0.03 / 0.00002 = 1,500 kgm-3
Relative density
This is the density of a substance compared to the density of water.
It is symbolized by (d) and has no units since it’s a ratio.
Relative density (d) = density of substance / density of water. It is measured using a relative density bottle
Example
The relative density of some type of wood is 0.8. Find the density of the wood in kg/m 3.
Solution
Density of substance = d × density of water
Density of subs tance = 0.8 × 1,000 = 800 kgm-3
Densities of mixtures
We use the following formula to calculate densities of mixtures
Density of the mixture = mass of the mixture / volume of the mixture
Example
100 cm3 of fresh water of density 1,000 kgm-3 is mixed with 100 cm3 of sea water of density 1030 kgm-3.
Calculate the density of the mixture.
Solution
Mass = density × volume
Mass of fresh water = 1,000 × 0.0001 = 0.1 kg
Mass of sea water = 1030 × 0.0001 = 0.103 kg
Mass of mixture = 0.1 + 0.103 = 0.203 kg
Volume of mixture = 100 + 100 = 200 cm3 = 0.0002 m3
Therefore density = mass / volume = 0.203 / 0.0002 =1,015 kg/m3.
Time
This is a measure of duration of an event . The SI unit for time is the second (s). Sub- multiples of the second are milliseconds, microseconds, minute, hour, day, week and year.
It is measured using clocks, stop watches, wrist watches, and digital watches.
Accuracy and errors
Accuracy is the closeness of a measurement to the correct value of the quantity being measured.
It is expressed as an error.
An error is therefore the deviation of measurement to the correct value being measured.
The smaller the error the accurate the measurement.
% error = (sensitivity / size measured) × 100.
Chapter Three
Forces.
Force is a push or a pull. Force is therefore that which changes a body’s state of motion or shape.
The SI unit for force is Newton (N). It is a vector quantity. It is represented by the following symbol.
Types of forces1. Gravitational force –this is the force of attraction between two bodies of given masses.
- Earth’s gravitational force is the force which pulls a body towards its center. This pull of gravity is called weight.
2. Force of friction – this is a force which opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact with each other. Friction in fluids is known as viscosity.
3. Tension force – this is the pull or compression of a string or spring at both its ends.
4. Upthrust force – this is the upward force acting on an object immersed in a fluid.
5. Cohesive and adhesive forces – cohesive is the force of attraction of molecules of the same kind while adhesive is the force of attraction of molecules of different kinds .
6. Magnetic force – this is a force which causes attraction or repulsion in a magnet.
7. Electrostatic force – this is the force of attraction or repulsion of static charges.
8. Centripetal force – this is a force which constrains a body to move in a circular orbit or path.
9. Surface tension – this is the force which causes the surface of a liquid to behave like a stretched skin. This force is cohesive.
Factors affecting surface tension
a) Impurities – they reduce the surface tension of a liquid i.e. addition of detergent.
b) Temperature – rise in temperature reduces tension by weakening inter-molecular forces.
Mass and weight.
Mass is the amount of matter contained in a substance while weight is the pull of gravity on an object.
The SI unit for mass is the Kg while weight is the newton (N).
Mass is constant regardless of place while weight changes with place.
The relationship between ma ss and weight is given by the following formula, W = mg where g = gravitational force.
Differences between mass and weightMass
An astronaut weighs 900 N on earth. On the moon he weighs 150 N. Calculate the moons’ gravitational strength. (Take g = 10 N/kg).
Solution
Moons’ gravitational strength = weight of astronaut on the moon / mass of astronaut. = 150 / 90 = 1.67 Nkg-1.
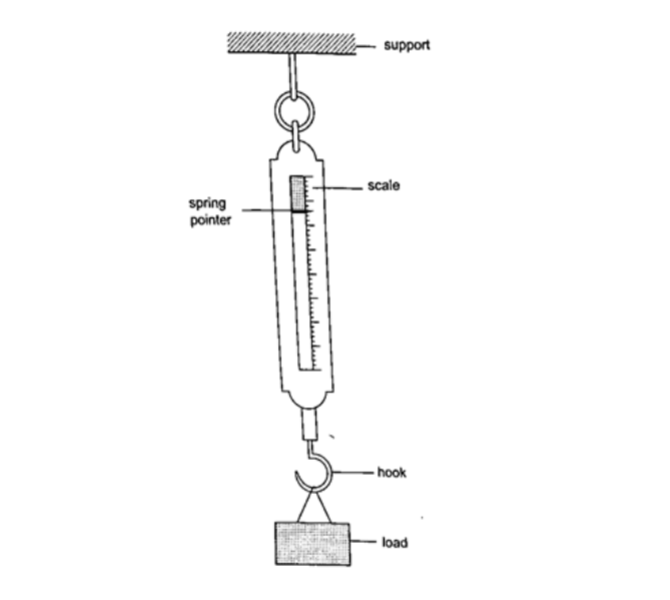
Measuring force
We use a spring balance to measure force. A spring balance is an instrument that uses the extension of a spring to measure forces.
ExampleThe length of a spring is 16.0 cm. its length becomes 20.0 cm when supporting a weight of 5.0 N. calculate the length of the spring when supporting a weight of:
a) 2.5 N
b) 6.0 N
c) 200 N
Solution
5N causes an extension of 4.0 cm, therefore 1.0 cm causes an extension of 4 /5 = 0.8 cm.
a) 2.5 N => 2.5 × 0.8 = 2.0 cm therefore length becomes = 16.0 + 2.0 = 18.0 cm.
b) 6.0 N => 6.0 × 0.8 = 4.8 cm therefore length becomes = 16.0 + 4.8 = 20.8 cm.
c) 200 N => 200 × 0.8 = 160.0 cm therefore length becomes = 16.0 + 160.0 = 176.0 cm.
Vector and scalar quantities
A scalar
quantity is a quantity which has magnitude (size) only . Examples are distance, mass, speed
A vector
quantity is a quantity which has both magnitude and direction. Examples are displacement, weight, velocity.
chapter Four
Pressure
Pressure is defined as the force acting normally (perpendicularly) per unit area .
The SI units for pressure is newton per metre squared (N/m2).
One Nm-2 is known as one Pascal (Pa).
Pressure = normal force / area or pressure = thrust / area . Another unit for measuring pressure is the bar. 1 bar = 105 N/m2. 1 millibar = 100 N/m2.
Calculating pressure
Examples
1. A rectangular brick of weight 10 N, measures 50 cm × 30 cm × 10 cm.
calculate the values of the maximum and minimum pressures which the block exert when resting on a horizontal table.
Solution
Area of the smallest face = 0.3 × 0.1 = 0.03 m2. Area of the largest face = 0.5 × 0.3 = 0.15 m2.
Maximum pressure = 10 N / 0.03 = 3.3 × 102 N/m2. Minimum pressure = 10 N / 0.15 = 67 N/m2.
2. A man of mass 84 kg stands upright on a floor. If the area of contact of his shoes and the floor is 420 cm2, determine the average pressure he exerts on the floor. (Take g = 10 N/Kg)
Solution
Pressure = force / area = 840 / 0.042 = 20,000 Nm-2.
Pressure in liquids.
The following formula is used to determine pressure in liquids.
Pressure = h ρ g, where h – height of the liquid, ρ – density and g – is force of gravity.
Examples
1. A diver is 10 m below the surface of water in a dam. If the density of water is 1,000 kgm -3, determine the pressure due to the water on the diver. (Take g = 10 Nkg-1)
Solution
Pressure = h ρ g = 10 × 1000 × 10 = 100,000 Nm-2.
2. The density of mercury is 13,600 kgm-3. Determine the liquid pressure at a point 76 cm below the surface of mercury. (Take g = 10 Nkg-1)
Solution
Pressure = h ρ g = 0.76 × 13,600 × 10 = 103,360 Nm-2
. 3. The height of the mercury column in a barometer is found to be 67.0 cm at a certain place.
What would be the height of a water barometer at the same place? (Densities of mercury and water are 1.36 × 104 kg/m3 and 1.0 × 103 kg/m3 respectively.)
Solution
Let the pressure due to water be h1ρ1g1= h ρ g, hence;
h1 = h ρ / ρ1= (6.7 × 10-1) × (1.36 × 104) = 911.2 cm or 9.11 m.
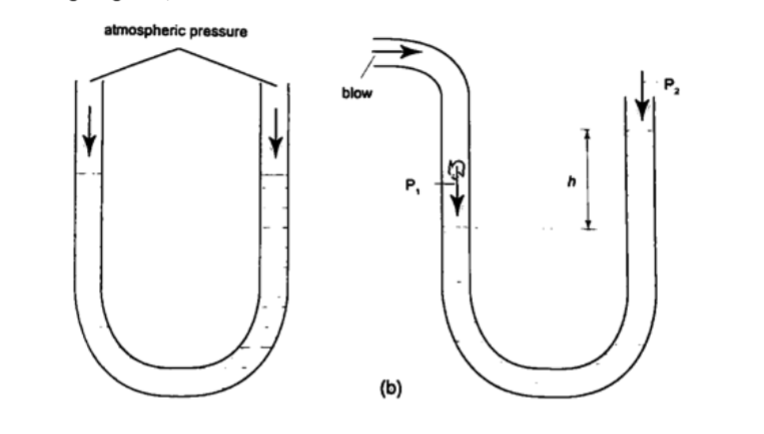
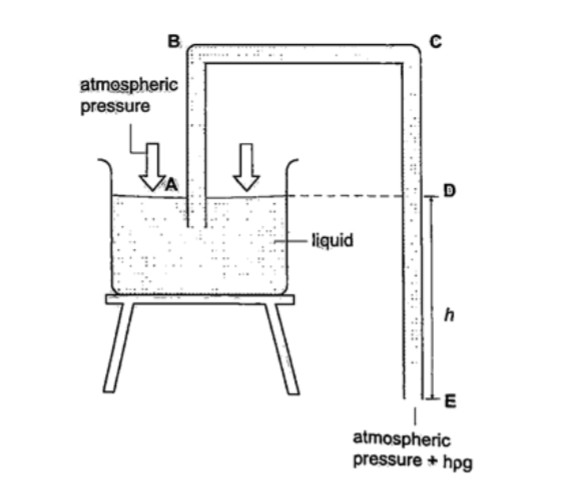
U-tube manometer
It is a transparent tube bent into U-shape. When a liquid is poured into a u-tube it settles at equal level since pressure depends on height and they s hare the same bottom.
Consider the following diagrams;
For the levels to differ the pressure P1 must be greater than P2, henceP1 = P2 + hρg.
If P1 is the lung pressure, P0 is the atmospheric pressure, then if the difference is ‘h’ then lung pressure can calculated as follows.
P1 = P0 + hρg.
Example
A man blows into one end of a U-tube containing water until the levels differ by 40.0 cm. if the atmospheric pressure is 1.01 × 105 N/m2 and the density of water is 1000 kg/m3, calculate his lung pressure.
Solutionp Lung pressure = atmospheric Pressure + liquid pressure
P1 = P0 + hρg. Hence P1 = (1.01 × 105) + (0.4 × 10 × 1000) = 1.05 × 105 N/m2.
Measuring pressure
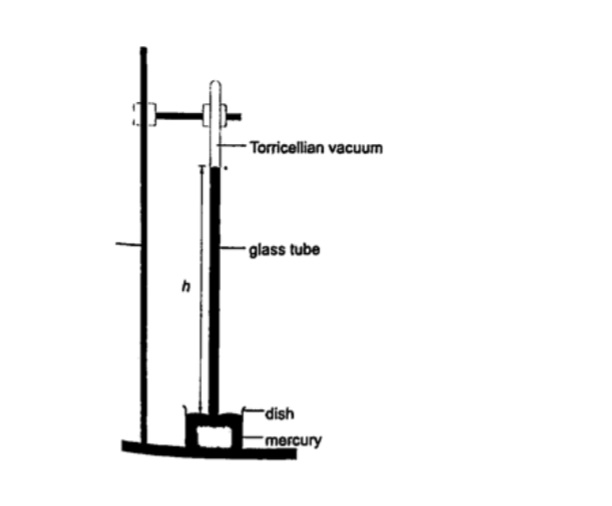
1. Simple mercury barometer– it is constructed using a thick walled glass tube of le ngth 1 m and is closed at one end. Mercury is added into the tube then inverted and dipped into a dish containing more mercury. The space above the mercury column is called torricellian vacuum.
The height ‘h’ (if it is at sea level) would be found to be 760 mm.
Atmospheric pressure can be calculated as, P = ρ g h =>where ρ (mercury)- 1.36 × 104 kg/m3, g- 9.81 N/kg, h- 0.76 m. Then P = (1.36 × 104) × 9.81 × 0.76 = 1.014 × 105 Pa.
NOTE- this is the standard atmospheric pressure, sometimes called one atmosphere. It is approximately one bar.
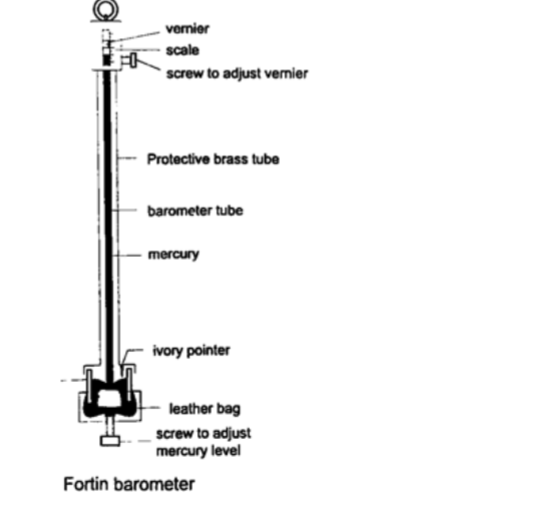
2. Fortin barometer–this is a more accurate mercury barometer. The adjusting screw is adjusted first to touch the mercury level in the leather bag.
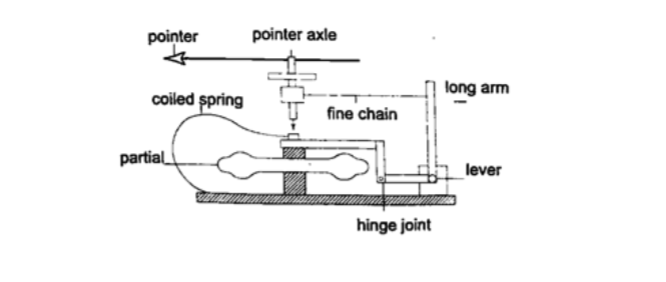
3. Aneroid barometer– increase in pressure causes the box to contract, the movements are magnified by the system of levers and is transmitted to the pointer by the fine chain and this causes the pointer to move.The scale is suitably calibrated to read pressure. Since pressure falls or rises as altitude falls or rises, the pointer can also be calibrated to read altitude.
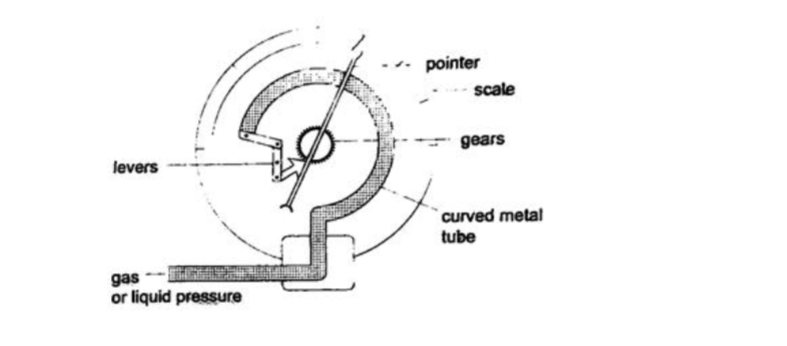
4. Bourdon gauge– it is also called gauge pressure and is used in gas cylinders. When air is blown into the rubber tube, the curved metal tube tries to straighten out and this causes movement which is transmitted by levers and gears attached to a pointer. This gauge can measure both gas and liquid pressure.
Examples1. The height of the mercury column in a barometer is found to be 67.0 cm at a certain place.
What would be the height of a water barometer at the same place? (densities of mercury - 1.36 × 104 kg/m3 and water- 1.0 × 103 kg/m3).
Solution
Let the pressure due to water be h1 ρ1 g1and that of water be h ρ g. Then h1 ρ1 g1= h ρ g. Hence h1 = (6.7 × 10-1) × (1.36 × 104) / 1.0 × 103 = 911.2 cm or 9.11 m.
Application of pressure in gases and liquids.
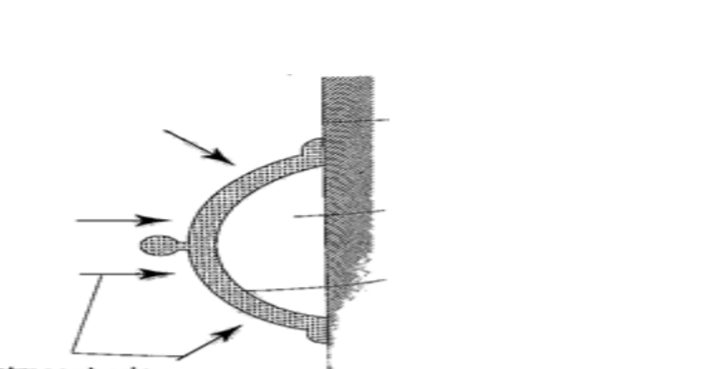
1. Rubber sucker– this is a shallow rubber cap. Before use it is moistened to get a good seal then pressed firmly on a smooth surface so that the air inside is pushed out. The atmospheric pressure will then hold it firmly against the surface as shown below.
They are used by printing machines to lift papers, lifting glass panes, heavy metal sheets etc.
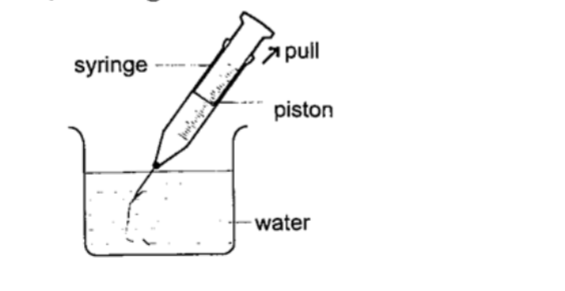
2. Drinking straw– when a liquid is drawn using a straw air is sucked through the straw to the lungs. This leaves the space in the straw partially evacuated. The atmospheric pressure pushing down the liquid in the container becomes greater than the pressure inside the straw and this forces the liquid into your mouth.3. The syringe– they work in the principle as the straw. They are used by the doctors in hospitals for giving injections.
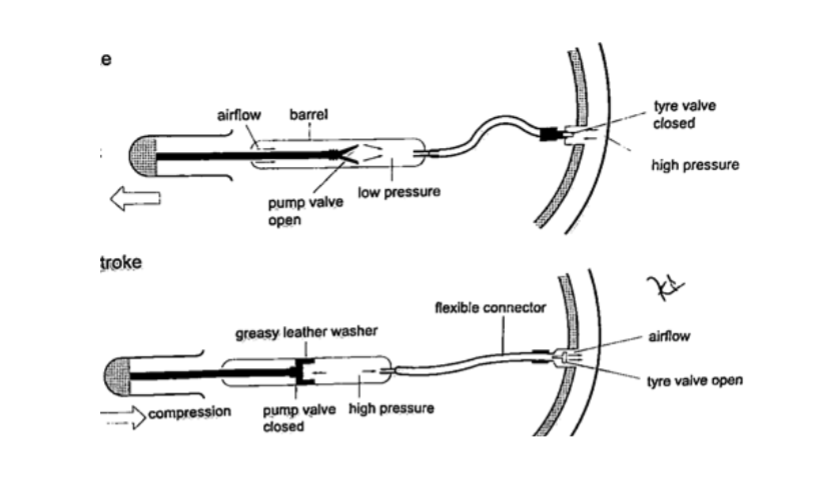
4. Bicycle pump– it uses two valves, one in the pump (greasy leather) and the other in the tire. When the handle is pushed in, the pressure inside the barrel becomes greater than the one in the tire and this pushes air inside.The valve in the tire is made such that air is locked inside once pumped.
5. The siphon– it is used to empty tanks which may not be easy to empty by pouring their contents out.The tubing must be lowered below the base of the tank.
The liquid flows out due to pressure difference caused by the difference in height ( h ρ g).
6. Lift pump.7. Force pump.
Transmission of pressure in liquids and gases.
It was first recognized by a French mathematician and physicist called Blaise Pascal in the 17th century.
Pressure is equally distributed in a fluid and equally transmitted as shown in
the following,
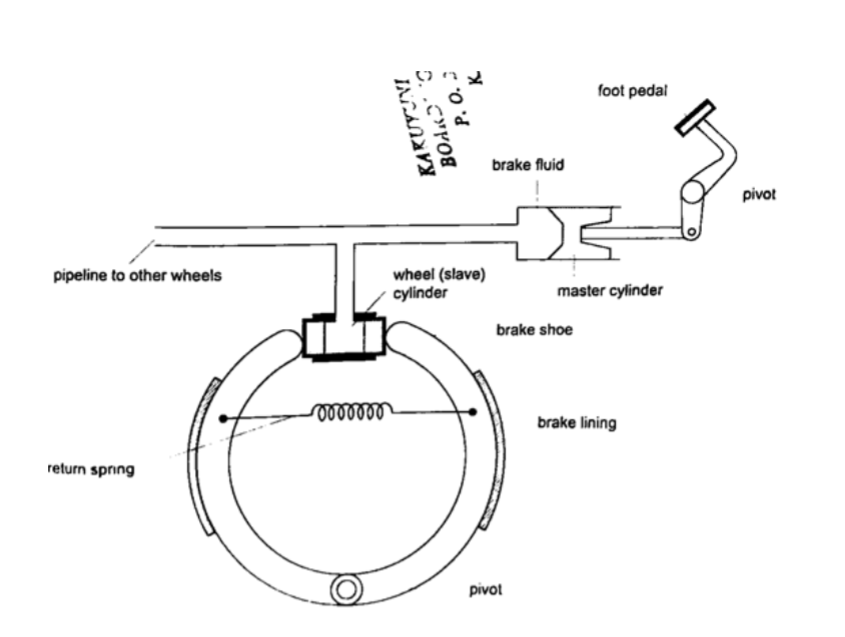
a) Hydraulic brake system– the master cylinder transmits pressure to the four slave cylinders on each wheel.
The cylinders contain brake fluid.
Fluid is used because liquids are almost incompressible.
When force is applied in the pedal the resulting pressure in the master cylinder is transmitted to the slave cylinders.
This forces the piston to open the brake shoes which then pushes the brake lining against the drum.
This force the rotation of the wheel to slow down. It is important to note that pressure is equally distributed in all wheels so that the car doesn’t pull or veer to one side.
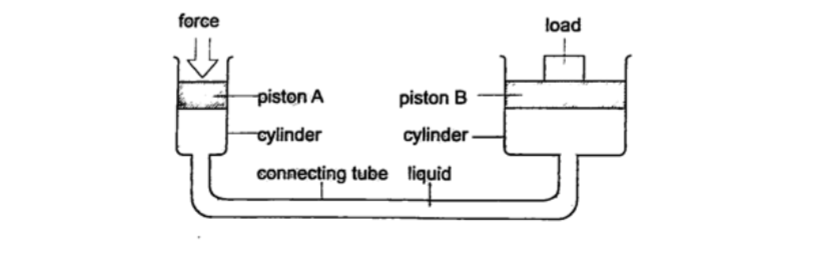
b) Hydraulic press– it consists of two pistons with different cross -sectional areas. Since pressure is transmitted equally in fluids, when force is applied in one piston it is transmitted to the other piston.The smaller piston is called the force while the bigger piston is called the load.
They are used to lift heavy loads in industries, bending metals and sheets etc.
Examples1. The area of the smaller piston of a hydraulic press is 0.01 m 2 and that of the bigger piston is 0.5 m2. If the force applied to the smaller piston is 2 N, what force is transmitted to the larger piston?
Solution
Pressure = force / area – hence P = 2 / 0.01 = 200 Pa.
Force = Pressure × Area = 200 × 0.5 = 100 N.
2. The master cylinder piston in a car braking system has a diameter of 2.0 cm.
The effective area of the brake pads on each of the four wheels is 30 cm 2.
The driver exerts a force of 500 n on the brake pedal. Calculate.
a) The pressure in the master cylinder.
b) The total braking force in the car.
Solution
a) Area of the master cylinder – π r2 = 3.14 cm2
Pressure = force /area = 500 / 3.14 × 10-4 = 1.59 × 106 N/m2
b) Area of brake pads = (30 × 4) cm2. Since pressure in the wheel cylinder is the same as in the master cylinder)2
F = Pressure × Area = (1.59 × 106) × (120 × 10-4) = 1.91 × 104 N.
Chapter Five
Particulate Nature of Matter.
States of matter
Matter is anything that occupies space. Matter exists in three states: solids, liquids and gases.
Matter can be changed in various ways which includes physical, chemical and nuclear changes.
a) Physical changes– they are normally reversible and no new substances formed. Examples are;
(i) Change of state such as melting and vaporization
(ii) Thermal expansion due to heating
(iii) Dissolving solids in liquids
(iv) Magnetizing
(v) Charging electrically
b) Chemical changes– they are irreversible and new substances are formed Examples are;
(i) Changes caused by burning
(ii) Changes occurring in some chemicals due to heating e.g. mercuric oxide
(iii) The reactions resulting from mixing chemicals to form other substances.
c) Nuclear changes– these are changes occurring in nuclear substances which give off some particles i.e. Uranium and Radium. As this happens they change into other substances.
Particulate nature of matter
Matter is made up of millions of tiny particles which cannot be seen with naked eyes. These particles are called atoms and are made up of sub-atomic particles called protons, neutrons and electrons.
Atoms join together to form molecules.
Movement of particles
Particles move from one region to another by the process of diffusion. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration until an equilibrium is reached or achieved. Gases diffuse faster or readily than liquids.
The rate of diffusion depends on the manner of arrangement of individual particles.
Solids
Individual atoms in solids have a small space between them hence their forces of attraction are very strong.
They vibrate in their fixed positions and this gives solids a fixed shape.
Liquids
Forces of attraction between liquid molecules are not as strong as in solids where motion is not restricted. They collide with each other as they move about.
They take the shape of the container they are put in hence have no definite shape.
Gases
Molecules of atoms in gaseous state are further apart experiencing very small forces of attraction.
This makes them almost completely free from each other.
We say they are independent in space. Gases have no definite shape and volume but they take up the space and volume of the container they are put in.
Chapter Six
Thermal Expansion.
Introduction
Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of a body. Both Celsius scale (0C) and Kelvin scale (thermodynamic scale) are used to measure temperature.
The Kelvin scale is also known as the absolute scale temperature and is measured from absolute zero (0 K).
Expansion of solids
When solids are heated they expand. The expansion is so small such that we can’t see them.
The following experiments will demonstrate actual expansion of solids.
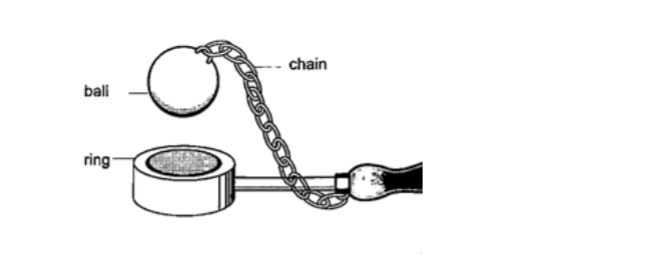
Experiment 1:- Ball and ring experiment
Procedure
1. Obtain a ball and ring apparatus.
2. Pass the ball through the ring at room temperature and observe that it easily slips through.
3. Heat the ball using a Bunsen burner for one minute.
4. Try to pass the ball through the ring and observe what happens.
5. Let it cool for some time and try passing the ball again.
DiscussionWhen the ball is heated it expands and increases in diameter. This makes the ball not to pass through the ring. After cooling it is found that the ball slips through the ring easily again.
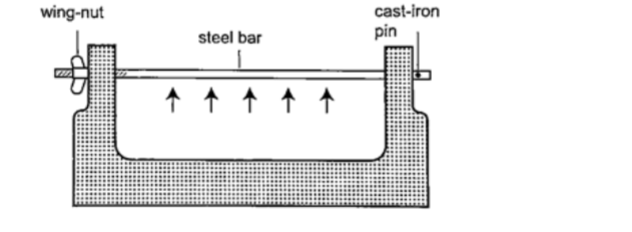
Experiment 2:
- The bar-breaker
Procedure
1. Try and break the cast-iron pin with your hands. Can you? (A bar-breaker is a strong iron frame which holds a steel bar fitted with a wing- nut. The other end is held by cast-iron pin as shown below).
2. Tighten the nut but do not break the pin.
3. Heat the bar strongly using two Bunsen burners as you keep tightening the nut. 4. Continue heating for another five minutes then let it cool.
5. Observe what happens.
DiscussionWhen the bar cools the cast-iron pin breaks. This shows that as the bar cools it contracts and strong forces pull against the pin.
These forces makes the pin to break.
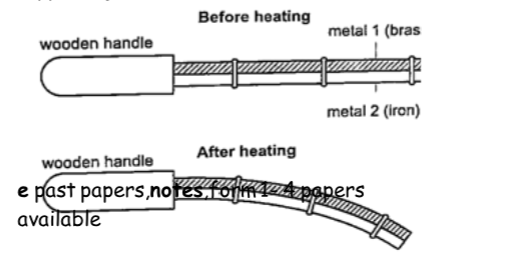
Experiment 3:- Heating a bimetallic strip
Procedure
1. Heat a brass-iron bimetallic strip using a Bunsen burner and make sure it is heated evenly.
2. Observe what happens after a short while.
DiscussionWhen a brass-iron bimetallic strip is heated it bends towards the iron.
This means that brass expands more than iron and this causes the strip to bend towards the iron side.
This shows that different materials expand at different rates when heated.
Applications of the expansion of solids
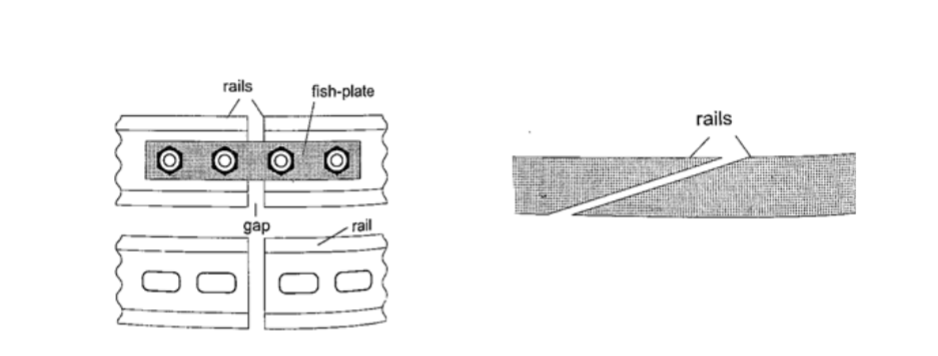
1. Construction of railway lines
– an expansion joint is allowed between any two rails to accommodate expansion.
A fish plate is used to join two rails. Modern railway system use the overlapping joint at the end of rails.
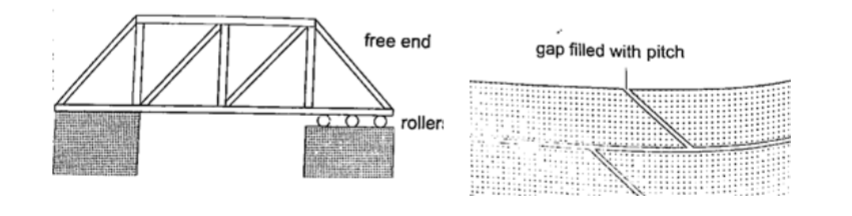
2. Construction of bridges and roof tops (steel girders)– for bridges one side has rollers while the other is fixed to allow for expansion.Concrete slabs are also laid on the ground leaving space filled with pitch to allow for expansion.
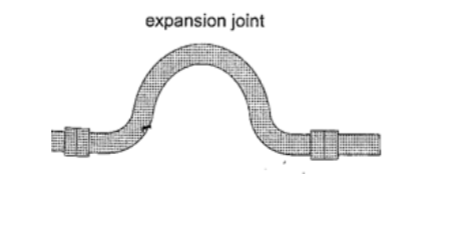
3. Hot water pipes– pipes carrying hot water (steam) from boilers are fitted with expansion joints for expansion.
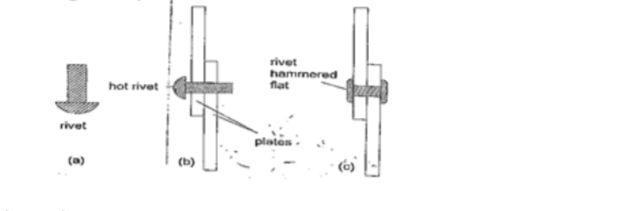
4. Riveting– used to join two pieces of metal together i.e. bimetallic strips, car bodies, drums etc.
Fitting rail cart wheel using heat uses the principle of rivets. Bimetallic strips are used in thermostats (control temperature) – electric iron box, alarm systems, car flasher units etc.
Expansion of liquids and gases.Expansion of liquids.
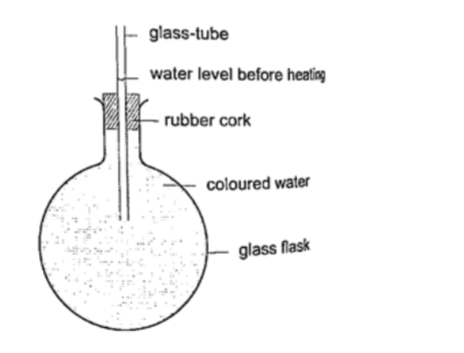
Liquids expand more than solids so it is easy to observe and see clearly as they expand. We use the hot water bottle to demonstrate the expansion of water. Water is put in the bottle as shown below.
When the bottle is immersed in hot water, initially there i s a drop in the level of water in the glass tube then it steadily rises after a while.This shows that liquids expand with increment in volume as shown by the hot water bottle.
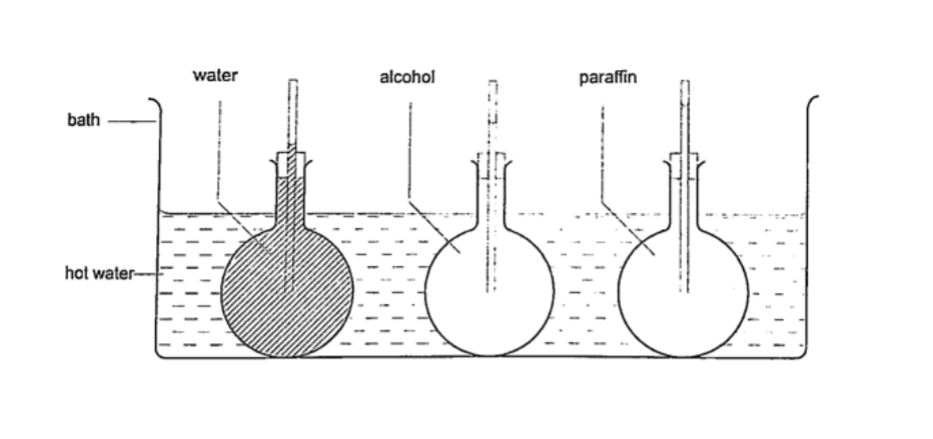
Different liquids expand at different rates as shown below.
Expansion of gasesThey are the easiest to observe since they expand the most.
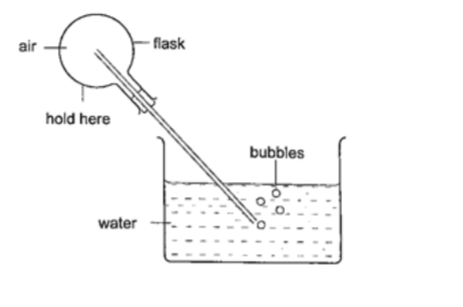
Experiment: - Expansion of air
Procedure
1. Obtain an empty 500 ml round bottomed flask fitted with a cork and a glass tubing.
2. Place a beaker with some water on a bench.
3. Rub your hands together thoroughly and place them on the flask and place it in the water as shown.
4. Observe what happens.
DiscussionThe heat produced by the hands makes the air inside the flask to expand.
This makes the volume to increase and therefore force the excess air out as bubbles.
Applications of the expansion of gases and liquids.
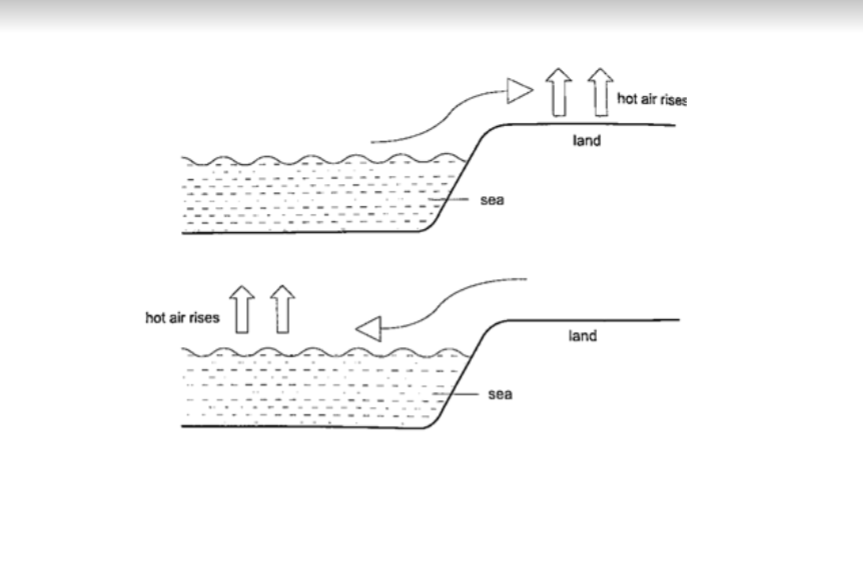
1. Land and sea breeze
– during the day the land is heated by the sun causing the air above it to expand.
The air becomes less dense therefore it rises. The space left is quickly filled by another cool air (generally from the sea since the land gets hot faster).
This causes a cool breeze form the sea during the day. At night the land loses heat faster than the sea.
The air above the sea rises since it is less dense and cool air from the land rushes to fill the gap.
This causes a breeze blowing from the land to the sea.
Thermometers1. Liquid-in-glass thermometer–this applies to the expansion of a liquid in a thin-walled glass-tube. The liquid moves up the tube when the bulb is heated.
The liquid must be a good conductor, visible and be able to contract and expand quickly and uniformly over a wide range of temperatures. It should also not stick on the sides of the tube. Liquids commonly used are mercury and coloured alcohol.
The scale is obtained by choosing two temperature points called fixed points.
In Celsius lower point is taken to be 0oC (when placed in ice) and the upper point as 100oC (boiling steam).
The two points are therefore divided into 100 equal parts (calibration). The melting and boiling points of both mercury and alcohol are (-39 oC – 357 oC) and (-112 oC - 78 oC) respectively.
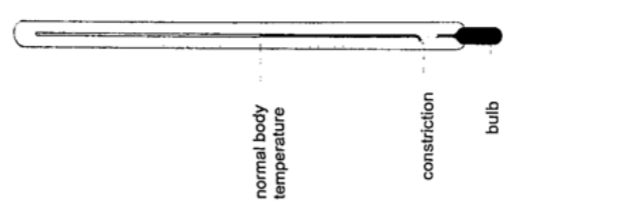
2. Clinical thermometer – this is a special type of mercury-in-glass thermometer used to measure body temperature. Since body temperature is normally 37 oC the scale is only a few degrees below and above 37oC.
It has a constriction which prevents mercury from going back after expansion for convenient reading of temperature.
This thermometer has a narrow bore for greater sensitivity and accuracy.
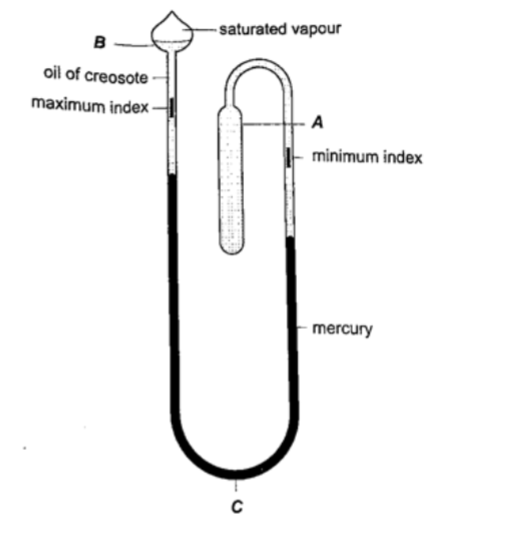
3. Six’s maximum and minimum thermometer – it is used to measure temperature of surroundings of an area or a place.It can record both maximum and minimum temperatures attained.
Consists of a large bulb (A) containing oil of creosote connected to U-shaped stem which connects to a second bulb (B) containing the same liquid.
The base (C) contains a thin thread of mercury. The range of this thermometer is between -20 oC and 50 oC. After each reading the indices are pulled down to the level of mercury by use of a magnet.
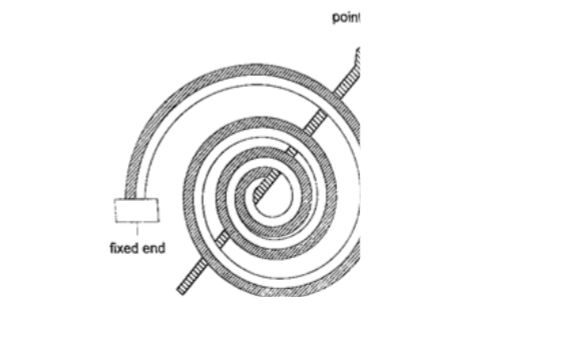
4. Bimetallic thermometer– it is made up of a bimetallic strip with one end fixed and the other connected to a pointer.Metals used are usually brass and invar.
As temperatures increase the strip unwinds and moves the pointer over a calibrated scale. It is used to measure high temperatures.
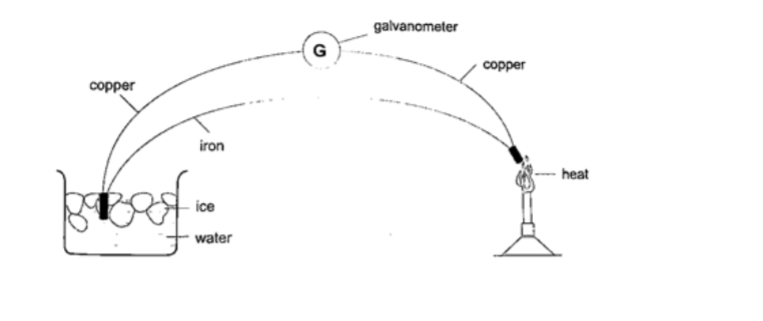
5. Thermocouple thermometer– thermocouple is a junction made of copper and iron looped at both ends. In practice a sensitive millivoltmeter is used instead of a galvanometer.A cold junction is maintained in melting ice (00C) while the other junction is heated steadily. This thermometer does not apply the principle of expansion.
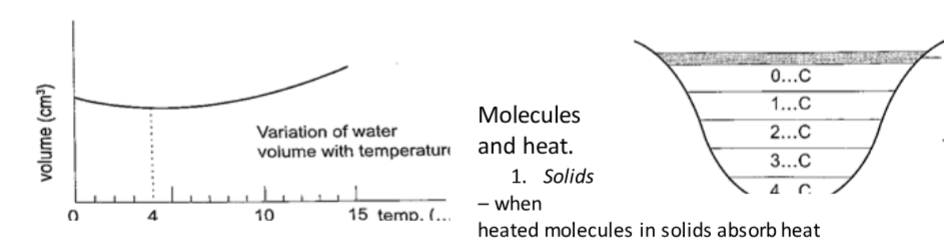
Unusual expansion of water.If water is heated let’s say from -150C it expands normally like any solid but only up to 0oC. At this point it starts to melt and it contracts.
This contraction will be observed up to 4 0C.
When heated further water starts to expand up to boiling point.
This is the unusual expansion of water.
This makes the top of water to freeze (0C) in temperate countries allowing the one below to remain liquid (40C). This supports marine life during winter.
Molecules and heat.1. Solids– when heated molecules in solids absorb heat energy and vibrate.
They push against one another and this causes expansion. Further expansion may result to collapse as melting in ice.
2. Liquids – besides vibrating particles in a liquid move short distances. As they move they collide by hitting each other and this results to more expansion.
For boiling to occur molecules absorb enough energy to be able to escape from the liquid.
3. Gases – individual particles are free of one another and in rapid motion.
When heated there are collisions with the walls of the container. This results to high pressure in the container.
Chapter Seven
Heat Transfer.
Heat is transferred in matter through the following methods: conduction, convection and radiation.
Conduction
This is the transfer of heat in solids. The rate of conduction depends on
1. Amount of temperature – the higher the temperature the higher the rate of transfer.
2. Cross-sectional area – the larger the cross-sectional area the higher the transfer.
3. Length of material – the shorter the material the higher the rate of transfer.
4. Type of material – different materials transfer heat at different rates.
Good and bad conductors
Conductivity is the ability of a material to conduct heat.
Good conductors of heat are those materials which are able to transfer heat easily and steadily.
Bad conductors are those which do not conduct heat.
Experiment:
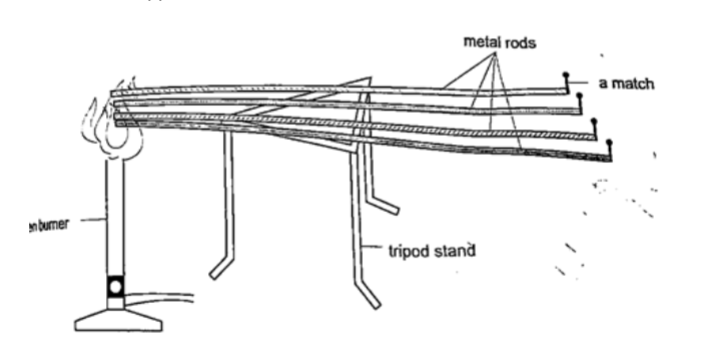
Comparing thermal conductivity of metals
Procedure
1. Obtain four identical rods of copper, iron, aluminium and brass.
2. At one end of each rod attach a matchstick using paraffin wax and let it solidify.
3. Place the rods on a tripod stand with the free ends close to one another as shown.
4. Heat the free ends strongly with a Bunsen burner.
5. Observe what happens.
DiscussionWhen done correctly and carefully the matchsticks will fall off in the following order: copper, aluminium, brass and finally iron. This shows that different metals conduct heat at different rates.
NOTE – on a cold morning a metallic chair would feel cold compared to a wooden chair at the same temperature, this is because the metal lic chair absorbs heat from your body as opposed to wood which is a bad conductor of heat.
Applications of conductors
Good conductors
1. They are used to manufacture cooking utensils
2. They are used as liquids suitable for thermometers i.e. mercury
3. Used as heat dumps (metal clips) when soldering delicate components in a circuit board i.e. transistors
Poor conductors
1. Used as insulators in handles of cooking utensils
2. Used in making good winter clothes i.e. wool
3. Hot water cylinders are lagged with fibre -glass since glass is a poor conductor of heat.
4. Houses in cold countries have double walls with air trapped in them to keep them warm.
Convection
This is the transfer of heat through fluids (liquids and gases). This occurs when part of the fluid is heated: they become less dense and rise above the cold fluid. As they move they carry heat with them.
In convection we observe streams of moving fluid called convectional currents.
Convection in air
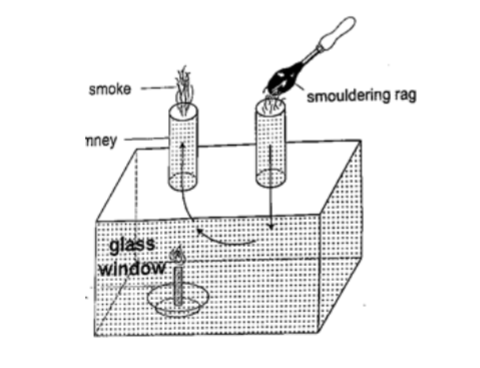
Experiment: model chimney (smoke box)
Procedure
1. Obtain a model chimney system or construct one as shown
2. Place a lighted candle under one of the chimneys
3. Place a smouldering cloth near the other chimney and observe what happens.
DiscussionSmoke will be seen going into the chimney and coming out through the other c himney. The air above the candle gets heated and rises up the chimney causing convectional currents which carry the smoke out with them.
Experiment: revolving paper-vane
Procedure
1. Make a paper-vane by cutting a thin card as shown
2. Put a string through the hole in the centre and hold it above a lighted Bunsen burner.
3. Observe what happens.
Discussion
As the air above the flame gets heated convectional currents are formed and rise upwards.as these currents brush against the paper-vane it rotates.
Convection in liquids
Experiment:
heating water in a beaker
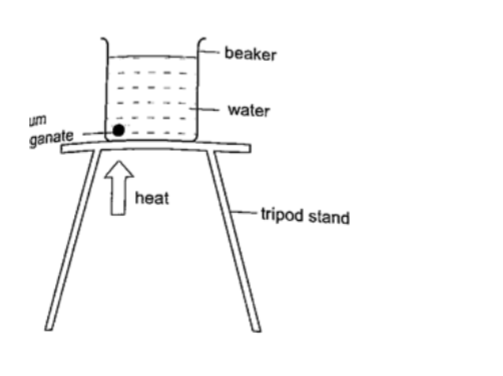
Procedure
1. Put water in a beaker until it is three quarters full and place it on a tripod stand.
2. Drop a crystal of potassium permanganate through a tube to settle at one corner at the bottom of the flask.
3. Heat the water gently using a Bunsen burner and observe the movement of streams of colour.
DiscussionA stream of colour will be seen moving upwards and downwards again at the other side of the beaker.
This will continue gradually until all the water becomes coloured. This shows that convectional currents also exist in liquids.
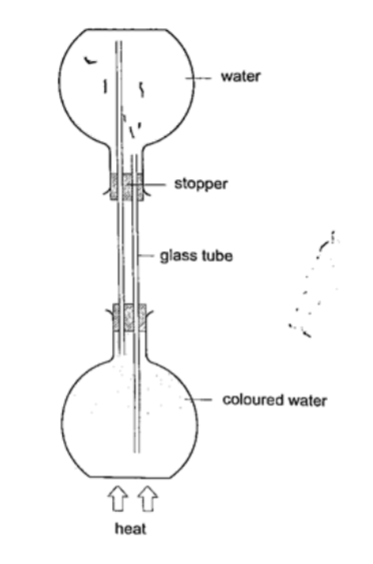
Experiment: model of hot water system
Procedure
1. Obtain two flat bottomed flasks and set up the apparatus as shown below.
2. Hold the flasks in place by use of clamp stands.
3. Heat the bottom of the lower flask and observe what happens.
DiscussionWhen the water in the lower flask becomes hot it rises up to the upper flask. After some time the water in the upper flask will become hot due to convectional currents.
Applications of convection
1. Brings about the land and sea breezes.
2. Can be used to explain the weather phenomena.
3. Used in car radiators.
4. Used in immersion water heaters by placing them at the bottom.
Radiation
This is simply the flow of heat from one point to another by means of electromagnetic waves.
Radiation from different surfaces
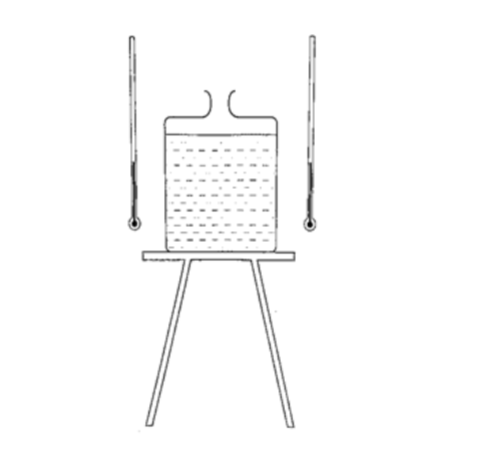
We use the Leslie cube to determine radiation of different surfaces.
It is a rectangular metal container of square base with small opening at the top.
One side is coated with polished silver, another dull black (candle flame soot), the other grey and the fourth white.
Experiment: Radiation from different surfaces
Procedure
1. Place a Leslie cube on a tripod stand and attach a thermometer on each of the four sides.
2. All thermometers should be at least 5.0 cm form the surface and should read the same temperature.
3. Pour hot water (about 80 0C) until it is full and note the reading of each thermometer after 1 minute.
4. Repeat the above procedure using boiling water (100 0C).
DiscussionThe thermometer against the black surface records the highest temperature, followed by the one on the grey side, then the white surface while the polished side recorded the lowest temperature.
The readings when the water is boiling were higher, indicating that radiation depends on temperature. It also depends on the nature of surface.
Applications of radiation
1. Electric kettles have a chrome coat to reduce radiation.
2. Electric iron are silver coated to minimize radiation.
3. Green houses use radiation (heat trap) to grow crops.
4. Clouds reflect radiation back to the earth hence cloudy nights are warmer than clear nights.
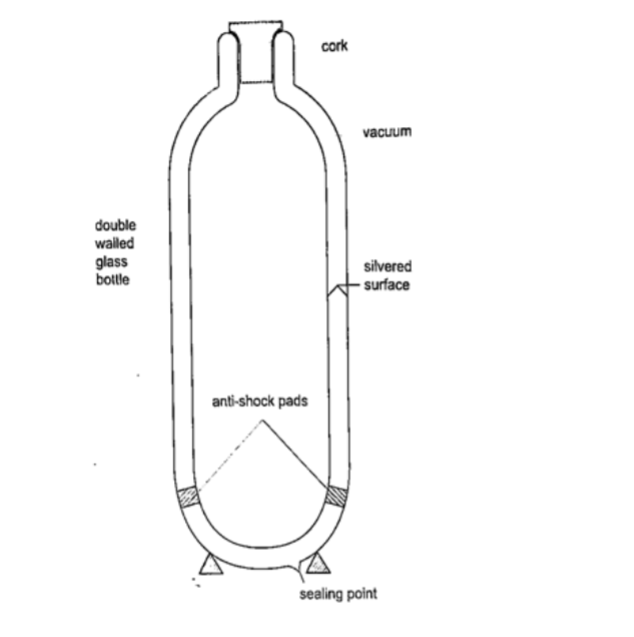
Vacuum flask
It was developed by Sir James Ivarin 1890. It keeps a liquid hot or cold (depends on what is put in).
The liquid stays at the temperature it is poured in either hot or cold.
It has the following principle features;
(i) The vacuum between the double walls
(ii) The two interior walls coated with silver
(iii) Insulating cork supports (anti-shock pads)
(iv) Insulating cork stopper at the top.
Chapter EightRectilinear Propagation and Reflection at Plane Surfaces. Introduction
Objects that produce their own light are known as luminous objects i.e. the sun, torch lamps etc. objects that do not produce their own light are called non-luminous objects i.e. the moon.
Opaque objects are those which do not allow light to pass through them. Translucent materials are those which allow light to pass through them but we cannot see through them i.e. church glass and bathroom glass.
Transparent materials are those which allow light to pass through them and we can see through them i.e. window panes, car windows etc.
A ray is the direction of the path followed by light. A beam is a group of rays travelling together.
Experiment: light travels in straight lines
Procedure
1. Obtain three cardboards with a hole at the center and mount them such that they form a straight line.
2. Arrange them as shown and place a lighted candle at one end and make sure that you can see the flame from the other end.
3. Move any of the cardboards and observe what happens.
Discussion
When one cardboard is displaced or moved slightly the flame cannot be seen at the other end. This shows that light travels in a straight line.
T his principle is applied in the following, Pinhole camera It consists of a closed box with a small hole on one face and a screen of tracing paper/ frosted glass on the opposite face as shown. An image will be formed on the screen.
Since light travels from one point of the object through the hole an image will be formed on the opposite screen of the box.
If the object is near the hole it is magnified while diminished if away from the hole.
Magnification is therefore the ration of the image to object height , expressed as,
Magnification = height of image/ height of object or
= distance of image from pinhole/ distance of object from pinhole
Shadows
Shadows are formed when an opaque object is placed between a source of light and a screen. When the shadow is big a dark patch at the centre is formed (umbra) while a surrounding lighter patch called penumbra is formed.
Eclipses Eclipse of the sun (solar eclipse) This occurs when the moon is between the earth and the earth.
The shadow of the moon falls on the earth’s surface. Sometimes the distance is large for the shadow to reach the earth and when this happens an annular eclipse occurs.
Annular eclipse
Eclipse of the moon
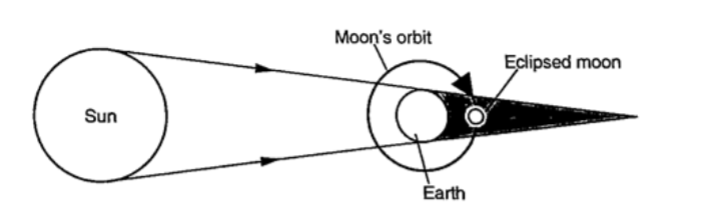
It is also known as lunar eclipse and occurs when the earth is between the sun and the moon. The shadow of the earth falls on the moon.
Examples1. Calculate the height of a building 300 m away from a pinhole camera which produces an image 2.5 cm high if the distance between the pinhole and the screen is 5.0 cm.
Solution
Object distance = 300 m, image height = 2.5 cm, image distance = 5.0 cm. Object
height/ image height = object distance/ image distance
Object height = (30,000 × 2.5) / 5.0 = 15,000 cm = 150 m.
2. The length of a pinhole camera is 25.0 cm. An object 2.0 cm is placed 10.0 m from the pinhole. Calculate the height of the image produced and its magnification.
Solution
Image height = (image distance × object height) / object distance
= (25 ×200) / 10 = 500 cm or 5 m. Magnification = image distance / object distance = 25 /10 = 2.5
Reflection from plane surfaces
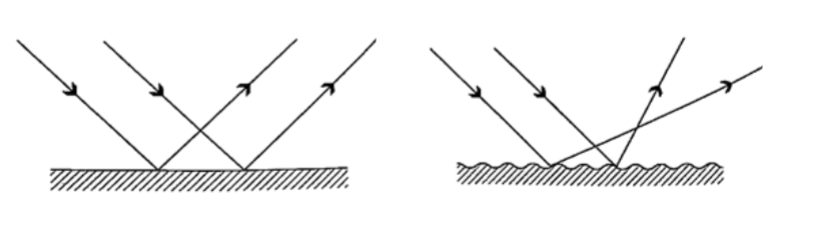
Diffuse and regular reflection
Regular reflection occurs when a parallel beam of light falls on a plane mirror band reflected as a parallel beam. They occur on polished surfaces. A diffuse reflection occurs on rough surfaces where a parallel beam of light is reflected in all directions.
Laws of reflection1. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray at the point of incidence must be on the same plane
2. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
I mages formed by reflection from plane surfaces
Characteristics of images formed in a plane mirror
1. The image is the same size as the object
2. The image is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front
3. The image is laterally inverted
4. The image is virtual
5. The image is erect.
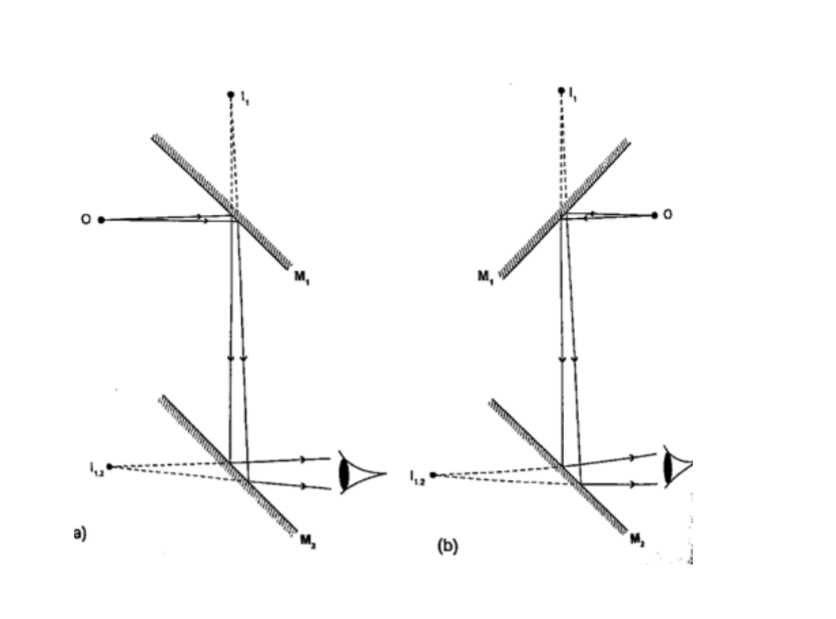
Location of an image by the non-parallax method
Parallax is the apparent relative motion of two objects due to the movement of the observer.
It only occurs when the objects are at a distance from one another.
This can be used to find the position of images in plane mirrors.
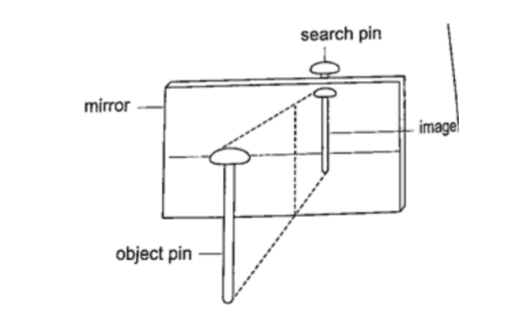
Experiment: To find the position of an image of a pin by non-parallax method
Procedure
1. Obtain a sheet of paper and draw a mirror line
2. Place the mirror on the line as shown
3. Place the pin at least 5 cm from the mirror and obtain another pin (search pin)
4. Move the pin till you get a point where there is no parallax and place your second pin.
5. Measure the distances (both image and object) and confirm your results.
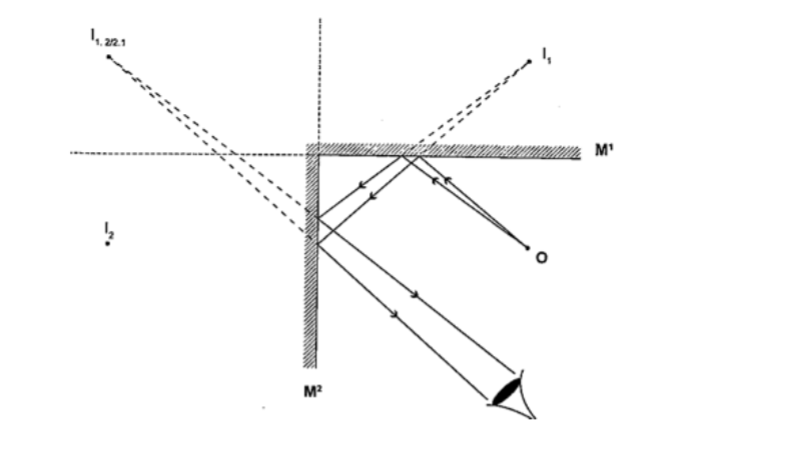
Mirrors at an angleWhen mirrors are placed at an angle several images are obtained depending on the angle between them.
If the angle is 600 the images formed will be five. We use the following formula to find the number of images.
n = (360o / θ) – 1
When mirrors are parallel then the images formed are infinite.
KaleidoscopeIt applies the principle of mirrors at an angle. Consists of two mirrors arranged at an angle of 600 to one another inside a tube.
The bottom has a ground-glass plate with brightly coloured glass for allowing light.
When one observes through the tube five images are seen.
The periscopeThis consists of two mirrors arranged at an angle of 450 as shown. This principle is used in periscopes (prisms) and telescopes.
Chapter NineElecrostatics I.
Some substances get charged when rubbed against other substances i.e. nylon, plastic, paper etc. the charge acquired stays within the body i.e. it does not move and therefore known as electrostatic charge or static electricity. The law of charges – types of charges There are two types of charges i.e. negative and positive charges.
The negative charge consists of electrons which are mobile.
The law of charges in summary states that “like charges repel, unlike charges attract’’.
Just like in magnetism attraction is not a sure way of testing for charge but repulsion because it will only occur if the bodies are similarly charged.
Charges, atoms and electrons
The atom is made up of a central part called the nucleus, containing positively charged ions called protons and outwardly surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
The nucleus also contain the particles called neutrons which are not charged.
When an atom is not charged the number of protons equals the number of electrons.
When a material is rubbed with another i.e. acetate with silk, electrons are transferred from one body to another.
The body accepting or receiving electrons becomes negatively charged while the one donating or losing electrons becomes positively charged.
Protons and neutrons in the nucleus do not move.
The SI unit for charge is the Coulomb (Coul.)
1 Coul. = charge on 6.25 × 1018 electrons. Charge on one electron = 1.60 × 10-19 Coul.
1 Coul. = 1 Ampere second (As).
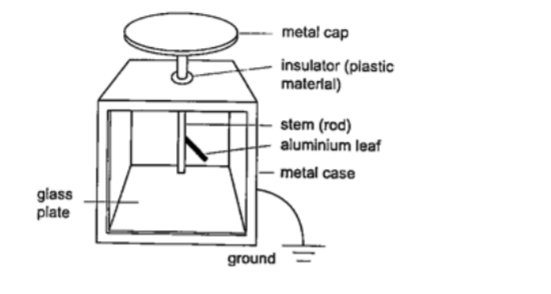
The leaf electroscope
This is a sensitive instrument for measuring charge .
It consists of a metal cap connected to a stem whose lower part is flattened into a plate with a thin strip of aluminium foil attached to it.
The plate and the leaf are enclosed in a metal casing which is earthed. The sides of the metal are made of glass to allow the leaf to be seen.
Other leaf electroscopes are made using gold strips and are referred to as gold leaf electroscope.Charging and discharging an electroscope
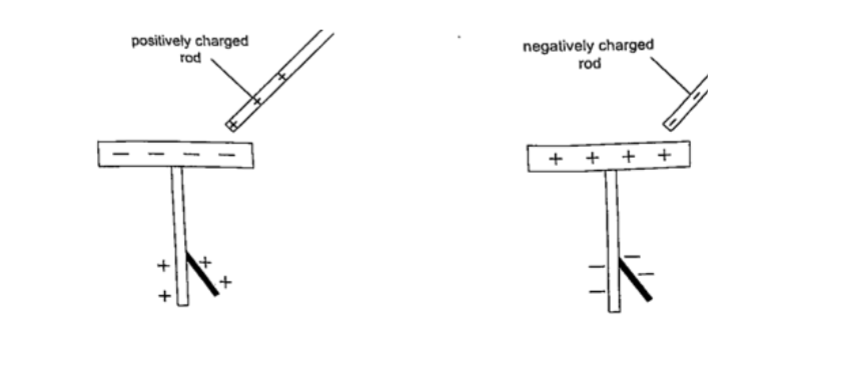
When a charged body is brought near the cap of the electroscope the leaf diverges, and when removed it collapses.
When a negatively charged body is brought near the metal cap electrons are repelled from the cap to the lower parts of the stem and the leaf.
This concentration of negative charges makes the leaf to diverge.
Similarly when a positively charged body comes near the metal cap the electrons are attracted by the protons and move up the stem, leaving a high concentration of positive charges which make the leaf to diverge.
If you touch the metal cap with your finger the leaf collapses showing that the charges have been discharged through your body.An uncharged body will always cause the leaf of a charged electroscope to collaps e regardless of the charge on the electroscope.
This shows that charge moves from the charged electroscope to the uncharged body.
Conductors and insulators
Conductors are those substances which allow easy passage of a charge. Insulators do not allow a charge to pass through easily .
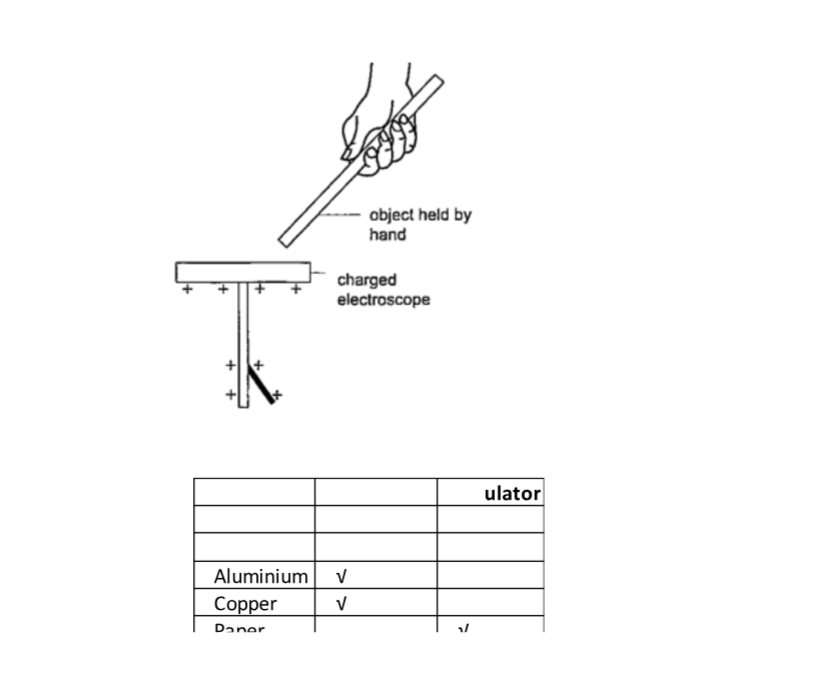
A charged electroscope can be used to classify objects into conductors and insulators.
Experiment: Arranging objects into conductors and insulators.
Procedure
1. Charge an electroscope by rubbing it with fur until its leaf diverges.
2. Obtain a number of materials like aluminium, paper, copper, iron, cloth, glass, wood etc.
3. Hold these items in your hand in turns and touch the charged electroscopes’ metal cap with it.
4. Record your results in the table shown below.
Charging an electroscope by inductionWe have seen that when a charged body is brought near a leaf electroscope, charges are transferred to the electroscope and the leaf diverges.
This method of transferring charge without actual contact is called induction.
Uses of the electroscope
1. To detect the presence of charge on a body.
2. To test the quantity of charge on a charge body.
3. To test for insulation properties of a material.
4. To test the sign of charge on a charged body.
Applications of electrostatic charges.
1. Electrostatic precipitator – they are used in chimneys to reduce pollution by attracting pollutants through electric ionization which then traps them by use of plates (wire mesh). Finger printing and photocopying uses the same principle.
2. Spray painting– as air cruises above the paint droplets acquire similar charges therefore spread out finely due to repulsion. Little paint is then used.
Dangers of electrostatics
As liquid flows through a pipe its molecules get charged due to rubbing against inner surface.
If the liquid is flammable then this can cause sparks and explode.
The same happens to fuels carried in plastic cans therefore it is advisable to carry fuel in metallic cans to leak out the continuously produced charges.
Chapter Ten
Cells and Simple Circuits.
Introduction
Work done per unit charge is called electrical potential. Current is the flow of charge.
For current to be continuous, potential difference between the two points must be sustained.
Sources of continuous currents.
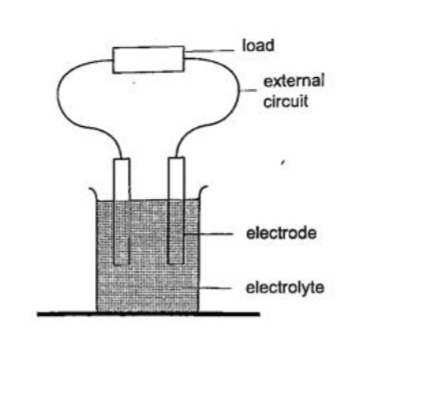
In this process work is continuously done in moving electrons against a repulsive force. A device in which the potential difference is sustained is called a cell .
A cell is a source of continuous current.
The end of a cell with a higher potential (fewer electrons)is called the positive terminal while the end with lower potential (higher electrons) is called the negative terminal.
1. Chemical sources
A good example is the electrochemical cell where simultaneous oxidation-reduction process occurs between the electrolyte and the electrodes.
An external circuit is used to transfer the electrons.
Examples of electro chemical cells are the primary cells i.e. the dry cell and Daniel cell.
The reactants must be replaced after supplying a given amount of energy. The second type is the secondary cell or storage cell where the chemical reaction is reversible i.e. the lead-acid battery and nickel-cadmium cell.
The third type is the fuel cell where chemical energy supplied is continuously converted into electrical energy i.e. hydrogen-oxygen cell used in spacecraft.
2. Thermoelectric sourcesA good example is the thermocouple where p.d is sustained by the continuous heating which keeps the terminals at different temperatures.
3. Solar sources
This occurs when some semi-conductor material called P and N type absorbs light at their transition region and gain energy enough to move electrons just like in cells.
They are used in spaceships, calculators, lighting, etc.
DC circuits
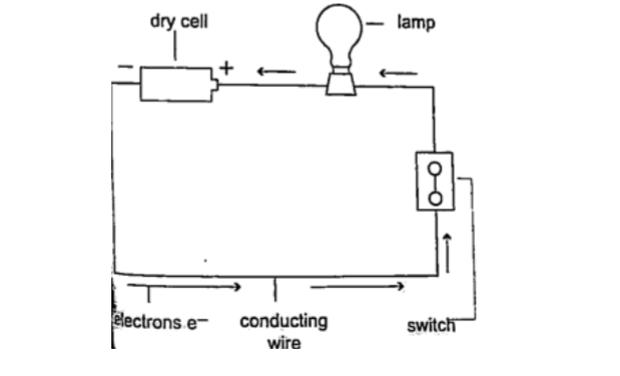
Conventionally current is a flow of positive charge and flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
A dc current is the flow of current in one direction that is from the positive terminal to the negative terminal when the loop is closed.
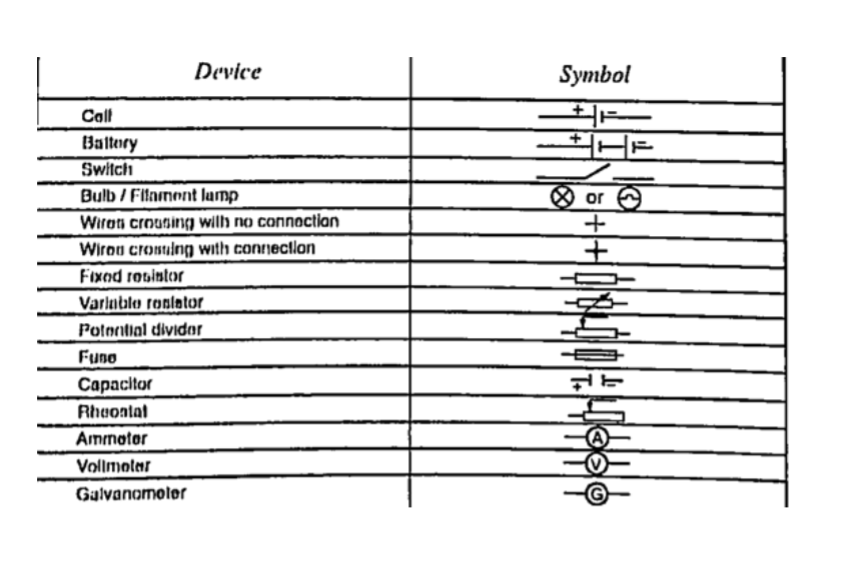
Circuit symbolsThe following symbols are used in electrical circuits.
Potential difference and currentPd is the work done by moving an electron from one point of a conductor to another. Current is by definition the rate of flow of charge.
Current = charge / time
The SI unit for current is the ampere, A.
1 A = 1 Coul/sec
1 milliampere (mA) = 10-3 A
1 microampere (µA) = 10-6 A
Examples
1. The current in a single loop is 3.0 A. How long would it take for a charge of 3600 coulombs to flow?
Solution Current = charge / time
Time = charge / current => 3600 / 3 = 1200 seconds = 20 minutes.
2.Primary cells
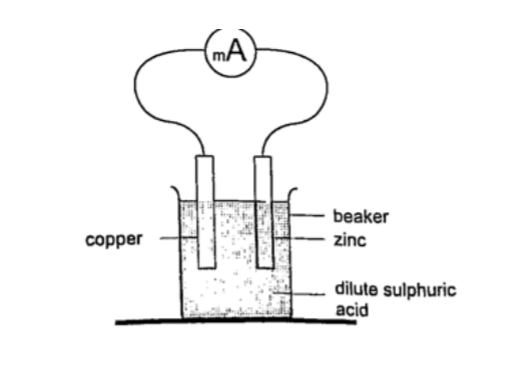
This is a cell formed by dipping two different metals into an electrolyte. Experiment: making a simple cell
Procedure
1. Take a piece of copper strip and zinc strip and clean thoroughly with emery paper.
2. Put the two strips in a beaker containing dilute sulphuric acid.
3. Observe what happens to the strips.
4. Connect the strips externally to a milliameter and a voltmeter.
DiscussionSulphuric acid is chemically written as, H2SO4 -----> 2H+ + SO42-
The electrons liberated by the acid move to the zinc electrode Zn ------> Zn2+ + 2e-
The hydrogen ions move to the copper strip
2H+ + 2e- ----> H2
Copper strip therefore becomes positively charged while the zinc becomes negatively charged electrode.
The accumulation of bubbles around the copper strip is called polarization.
The bubbles formed around the zinc strip is the reaction of acid with zinc impurities and is called local action.
Polarization produces insulation between the strip and the acid cutting off production of current eventually.
This is known as the internal resistance of the cell. Loc al action eats away the zinc strip and a mercury coat is applied to prevent this (amalgamation). Polarization and local action are the main defects of simple cells.
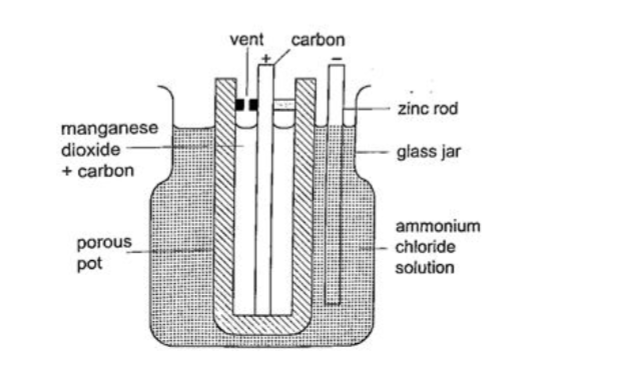
The Leclanche’ cell
In this cell carbon rod is used as the positive terminal and zinc as the negative electrode. The electrolyte is ammonium chloride solution (NH4Cl). No polarization since it is reduced by use of manganese (IV) oxide (MnO2) which oxidizes hydrogen into water. Local action still occurs. They are used in operating bells and telephone boxes.
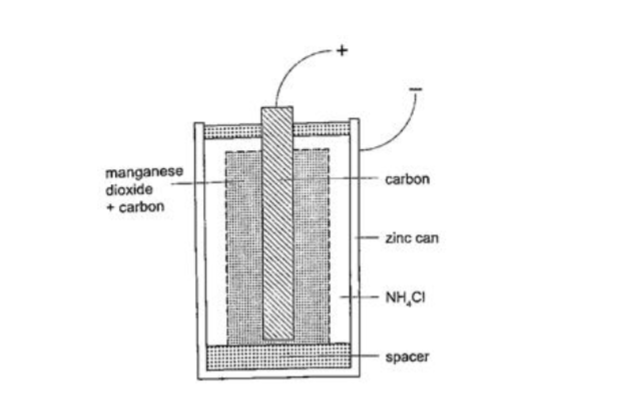
The dry cellIt is referred to as dry because it contains no liquid. The ammonium solution is replaced with ammonium chloride jelly or paste, the manganese (IV) oxide and carbon powder are used as the depolarizer.
The hydrogen gas produced is oxidized to water which eventually makes the cell wet after use. They are used in torches, radios calculators etc.
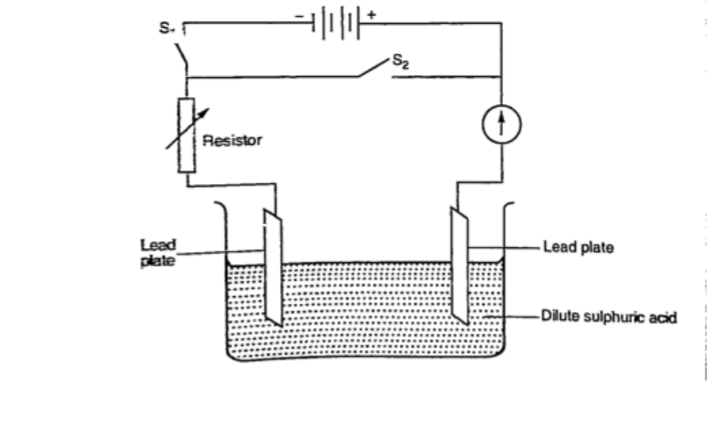
Secondary cellsThey are also called storage cells since they store electrical charge as chemical energy.
Experiment: To charge and discharge a simple secondary cell
Procedure
1. Set up the apparatus as shown below.
2. Close the switch S1 and observe the changes in the plates if any.
3. Note how the ammeter reading varies with time.
DiscussionWhen charging oxygen is produced at the anode and hydrogen at the cathode.
The oxygen reacts with lead to form lead (IV) oxide which is deposited at the anode.
The hydrogen formed has no effect.
When discharging current flows in opposite direction with oxygen be ing formed at the cathode and hydrogen at the anode.
The colour of the positive electrode changes from brown to grey.
Lead-acid accumulator.
A 12V accumulator has six cells connected in series. Each cell has several plates forming lattice grid with positive plates carrying lead (IV) oxide and the negative plates having spongy lead. They are placed close to one another with an insulating sheet separating them. They are rated in ampere-hours i.e. 30 Ah means that it can supply 1 ampere for 30 hours or 2 amperes for 15 hours etc.
Example
A battery is rated at 30 Ah. For how long will it work if it steadily supplies a current of 3 A?
Solution
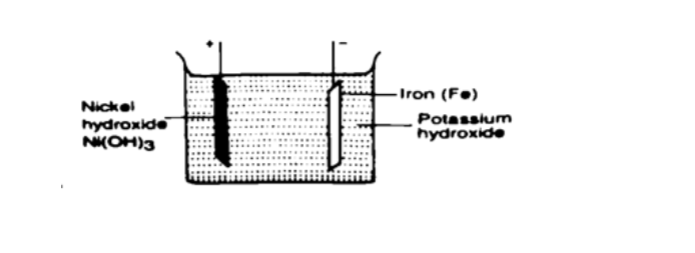
Q = I t, hence t = Q / I => 30 / 3 = 10 hours. Alkaline accumulators
Potassium hydroxide (KOH).Nickel hydr oxide (Ni (OH) forms the positive electrode while iron forms the negative electrode.
They are two types nickel cadmium (NiCd) and nickel iron (NiFe).
They are used in ships, hospitals and buildings where large currents are required for emergencies.
Advantages of alkaline accumulators over lead-acid accumulators1. Large currents can be drawn from them
2. They require little maintenance
3. They are portable
4. They can remain discharged for a long time without getting ruined.
Disadvantages
1. They are very expensive
2. They have lower e.m.f per cell.physics
Kenya Scholarships for Undergraduate Students » Kenya Scholarships for Postgraduate Students » Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyan Students »Kenya Undergraduate Scholarships » Full Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyans» Kenya Postgraduate Scholarships »Scholarships & Grants » Undergraduate Scholarships » Universities in Kenya »Kenya Universities and Colleges Central Placement Service (KUCCPS) » Colleges in Kenya » KASNEB Registration & Results » Secondary Schools Scholarships in Kenya » Undergraduate & Graduate Scholarships for Kenyans
Powerful Motivational Quotes for Students » Success Quotes for Students» KCSE Motivational Quotes for KCSE Candidates » KCSE Success Quotes for KCSE Candidates
a a a physics notes! chapter 1 introduction to physics college physics notes download klb physics book 4 download physics notes form 3 electronics form four notes form 1 past papers form 1 past papers with answers form 1 physics notes form 1 physics questions and answers form 1 physics revision notes form 1 physics syllabus form 1 physics test paper pdf form 2 physics exam paper form 2 physics exam paper 2016 form 2 physics exam paper free download form 2 physics exam paper with answer form 2 physics final year exam paper 2 form 2 physics past papers form 2 physics revision notes form 2 physics short notes form 2 physics syllabus form 3 past papers form 3 physics exam paper form 3 physics notes form 3 physics past papers form 3 physics questions form 3 physics questions and answers pdf form 3 physics revision notes form 3 physics syllabus form 4 exam papers form 4 physics notes form 4 physics revision notes form 4 physics syllabus form 4 physics topics form 5 physics topics form five physics notes form four physics notes form four physics questions and answers form four physics questions and answers pdf form four physics topics form four revision papers form one exams form one past papers form one physics examination form one physics past papers pdf form one physics questions and answers form one physics questions and answers pdf form one physics topics form one term one physics exam form three physics notes form three physics notes pdf form three physics questions and answers form three physics questions and answers pdf form three physics topics form two notes form two physics notes form two physics notes pdf form two physics questions and answers form two physics questions and answers pdf form two physics syllabus form two physics topics high school physics notes high school physics study guide introduction of physics form one introduction to physics notes k.l.b physics notes kcse physics notes kcse physics syllabus kenya secondary school physics syllabus pdf klb physics book 1 pdf klb physics book 2 pdf klb physics book 3 pdf klb physics book 3 pdf download klb physics book 4 notes klb physics book 4 pdf klb physics book 4 pdf download klb physics book 4 topics klb physics form 1 klb physics form 1 pdf klb physics form 2 klb physics form 2 notes klb physics form 2 pdf klb physics form 2 pdf download klb physics form 3 klb physics form 3 pdf klb physics form 3 pdf download klb physics form 4 klb physics form 4 pdf klb physics form four notes klb physics form one notes klb physics form three notes klb physics form two notes klb physics notes klb physics notes form 4 klb physics pdf maktaba tetea notes necta form four past papers necta past papers form 4 2016 necta past papers form six necta past papers form two necta physics past papers necta physics practicals necta questions and answers necta review questions notes za physics form one notes za physics form three past papers 2014 physic form 4 chapter 1 mind map physic notes physics book 4 pdf physics exam form three physics form 1 exams physics form 1 mid year exam physics form 1 past papers physics form 1 pressure physics form 1 questions and answers physics form 1 questions and answers pdf physics form 2 exam paper 2014 physics form 2 exams physics form 2 notes physics form 2 past papers physics form 2 pdf physics form 2 questions and answers physics form 2 questions and answers pdf physics form 3 exams physics form 3 notes pdf physics form 3 past papers physics form 3 questions and answers physics form 3 syllabus physics form 4 chapter 1 conversion of units physics form 4 chapter 1 exercise physics form 4 chapter 1 exercise and answers physics form 4 chapter 1 exercise pdf physics form 4 chapter 1 mind map physics form 4 chapter 2 physics form 4 chapter 2 exercise and answers physics form 4 chapter 2 exercise pdf physics form 4 chapter 2 experiment physics form 4 chapter 2 formula physics form 4 chapter 2 mind map physics form 4 chapter 2 momentum physics form 4 chapter 2 notes pdf physics form 4 chapter 2 objective questions and answers physics form 4 chapter 2 paper 2 physics form 4 chapter 2 slideshare physics form 4 chapter 3 physics form 4 chapter 3 questions and answers physics form 4 chapter 4 notes pdf physics form 4 chapter 5 light questions and answers physics form 4 chapter 5 notes pdf physics form 4 exam paper 1 physics form 4 exams physics form 4 exercise physics form 4 exercise pdf physics form 4 module with answer physics form 4 notes chapter 1 physics form 4 notes free download physics form 4 notes pdf physics form 4 paper 2 questions and answers physics form 4 past papers physics form 4 questions and answers physics form 4 revision notes physics form 5 chapter 1 exercise and answers physics form 5 chapter 1 notes pdf physics form 5 chapter 2 notes pdf physics form 5 chapter 2 slideshare physics form 5 chapter 3 notes pdf physics form 5 notes pdf physics form four book physics form four notes pdf physics form four questions physics form four study notes physics form four topics physics form one physics form one book physics form one notes physics form one notes pdf physics form one study notes physics form three book physics form three notes physics form three study notes physics form two book physics form two notes physics form two notes pdf physics form two questions physics form two study notes physics form two topics physics module form 5 physics notes physics notes for class 11 pdf physics notes for class 12 pdf physics notes form 1 free download physics notes igcse physics notes pdf physics simple notes physics spm notes download physics spm notes pdf physics spm questions physics study guide answers physics study guide pdf physics study guides radioactivity form four secondary physics notes pdf spm notes success physics spm pdf tahossa past papers
1 a a kcse past papers 2014 kcse marking schemes 2016 kcse papers 2016 kcse prediction questions 2018 kcse exam 2018 kcse questions a a kcse past papers advance-africa.com kcse rev quiz agriculture mock papers agriculture paper 2 questions and answers pdf alliance mocks 2017 ap biology essay questions and answers arabic exam 2016 arabic oral exam questions betrayal in the city essay questions and answers pdf betrayal in the city essay questions with answers betrayal in the city, ,,revision questions biology book 3 klb biology essay questions and answers form 4 biology essay questions and answers form 4 pdf biology essays pdf biology exam questions and answers pdf biology form 2 questions and answers pdf biology form 3 notes pdf biology form 3 questions and answers pdf biology form 3 syllabus biology form three reproduction biology form three-questions and answers biology kcse - kcse biology questions and answers - kcse biology essay questions and answers - kcse biology paper 1 2015 - kcse biology notes - kcse 2015 biology paper 2 - kcse biology practical 2015 - kcse biology practicals - kcse biology 2011
biology kcse 2017 biology kcse questions biology paper 1 questions and answers biology paper 2 questions and answers biology paper 3 questions and answers biology questions and answers for high schools biology questions and answers for high schools pdf biology questions and answers form 2 biology questions and answers multiple choice biology questions and answers on cells biology questions and answers online biology questions and answers pdf biology revision notes form 3 business past kcse past papers c.r.e form one notes pdf cambridge igcse computer science cambridge igcse computer science answers cambridge igcse computer science coursebook pdf download cambridge igcse computer science revision guide pdf cambridge igcse computer science study and revision guide pdf cambridge igcse computer science workbook - free download cambridge igcse computer science workbook pdf caucasian chalk circle essay questions chemistry paper 1 questions and answers chemistry paper 2 questions and answers chemistry paper 3 question and answer chemistry past papers form 1 chemistry past papers form 2 cie past papers computer science 0478 computer science igcse past papers xtremepapers computer science paper 2 2017 computer science past papers a level computer science past papers o level computer studies form 1 questions computer studies form 3 past papers computer studies past papers computer studies questions and answers pdf county mocks 2017 cre form 2 notes pdf cre form 3 notes cre form 3 notes pdf cre form 4 notes cre form 4 notes pdf cre form one notes cre kcse 2016 cre notes cre notes form 2 cre notes pdf cre paper 1 with answers cre paper 2 cre paper 2 topics cre preparation notes cre questions form one cre revision notes cre revision questions and answers download kcse past papers with answers dvance kcse past papers edexcel igcse computer science past papers english paper 3 question paper - 2014 kcse english paper 3 question paper - 2015 kcse english paper 3 question paper - 2016 kcse english paper 3 question paper - 2017 kcse english paper 3 question paper - 2018 kcse essay questions and answers on betrayal in the city essay questions based on betrayal in the city find download kcse past papers with answers - kcse past papers pdf download - kcse 2013 marking scheme - kcse mathematics past papers pdf - free kcse past papers and marking schemes - kcse mock papers pdf - kcse past papers 2014 pdf - kcse past papers 2015 - kcse past papers 2010 find kcse biology essay questions and answers - kcse biology practicals - kcse biology paper 1 2015 - biology essay questions and answers form 4 - kcse biology questions and answers - ap biology essay questions and answers - kcse biology notes - kcse biology paper 2 2012 - kcse biology paper 2 2015
form 2 biology questions and answers free kcse mocks 2015 free kcse past papers - kcse past papers - knec kcse online past papers - knec kcse results past papers free kcse past papers 2014 free kcse past papers kenya, free marking schemes, download ... free kcse past papers with answers free kcse questions and answers on chemistry free revision papers general biology test questions and answers general science questions and answers pdf history and government paper one topics history form one questions and answers pdf history paper 1 questions and answers history paper 2 questions and answers home science past papers igcse computer science book igcse computer science book pdf download igcse computer science notes igcse computer science paper 2 notes igcse computer science past papers igcse computer science past papers 2014 igcse computer science past papers 2017 igcse computer science pdf igcse computer science pre release material 2018 igcse computer science resources igcse computer science revision notes pdf igcse computer science workbook pdf igcse computer studies past papers interesting biology questions ire kcse past papers k.c.s.e cre paper 1 2017 k.c.s.e geography 2017 k.c.s.e mathematics paper 1 2017 k.c.s.e mocks 2018 k.c.s.e past papers 2014 kcpe 2018 predictions kcpe prediction questions kcse 2010 marking scheme kcse 2010 past papers kcse 2011 cre paper 1 kcse 2011 marking scheme kcse 2012 history paper 2 marking scheme kcse 2012 marking schemes kcse 2013 cre paper 1 kcse 2013 marking scheme kcse 2013 marking scheme pdf kcse 2014 kcse 2015 biology paper 2 kcse 2015 biology paper 3 kcse 2015 marking scheme kcse 2015 past papers kcse 2016 agriculture paper 2 kcse 2016 biology paper 1 kcse 2016 biology paper 2 kcse 2016 computer paper 1 kcse 2017 marking scheme kcse 2017 maths paper 1 kcse 2017 papers kcse 2017 papers and marking scheme kcse 2017 past papers kcse 2017 prediction pdf kcse 2018 cre prediction kcse 2018 leakage kcse 2018 marking scheme kcse 2018 papers kcse 2018 predictions kcse 2019 marking scheme kcse agriculture past papers kcse answers kcse arabic paper 1 kcse arabic paper 2 kcse arabic paper 3 kcse arabic paper 3 2016 kcse arabic past papers kcse biology 2011 kcse biology essay questions and answers kcse biology essay questions and answers - kcse revision questions and answers - kcse chemistry questions and answers - kcse revision papers with answers - kcse past papers with answers - download kcse past papers with answers - kcse questions on the river and the source - kcse revision notes
kcse biology essay questions and answers - kcse revision questions and answers - kcse chemistry questions and answers - kcse revision papers with answers - kcse past papers with answers - download kcse past papers with answers - kcse questions on the river and the source - kcse revision notes
kcse biology essay questions and answers pdf kcse biology essays kcse biology essays pdf kcse biology notes kcse biology paper 1 kcse biology paper 1 2017 kcse biology paper 1 2017 pdf kcse biology paper 2 2012 kcse biology paper 2 2015 kcse biology paper 2 2017 kcse biology paper 3 2016 kcse biology paper 3 past papers kcse biology past papers kcse biology past papers and answers kcse biology practical 2016 kcse biology practical past papers kcse biology practicals kcse biology questions and answers kcse biology questions and answers - kcse past papers biology - kcse biology essay questions and answers - kcse chemistry past papers - download kcse past papers with answers - k.c.s.e papers 2015 - k.c.s.e papers 2016 - kcse biology paper 1 2015 - kcse past papers 2015 - kcse past papers 2011 - kcse past papers 2016 - kcse past papers 2017 - 2017 kcse prediction questions - 2018 kcse prediction questions
kcse business paper 1 2016 kcse business past papers kcse business studies past papers kcse chemistry paper 1 2016 kcse chemistry paper 1 2017 kcse chemistry paper 3 2012 kcse chemistry past papers kcse chemistry past papers and answers kcse chemistry practical kcse computer studies paper 1 kcse computer studies paper 2 kcse computer studies paper 2 pdf kcse cre 2016 kcse cre paper 1 2013 kcse cre paper 1 2015 kcse cre paper 1 2016 kcse cre paper 1 2017 kcse cre paper 2 kcse cre paper 2 2016 kcse cre past papers kcse cre past papers and answers kcse english paper 3 2016 kcse english paper 3 2017 kcse essay questions in betrayal in the city kcse exam papers 2018 kcse exam papers answers kcse french paper 1 kcse french paper 2 kcse french past papers kcse general science syllabus kcse geography paper 2 2016 kcse history paper 1 2012 kcse history paper 2 2016 kcse history paper 2 2017 kcse kiswahili paper 1 2017 kcse marking scheme 2016 kcse marking schemes kcse marking schemes 2017 kcse marking schemes pdf kcse mathematics marking schemes kcse mathematics paper 1 2015 kcse mathematics paper 1 2016 kcse mathematics paper 2 2016 kcse mathematics past papers kcse mathematics past papers pdf kcse mock exams kcse mock papers 2015 kcse mock papers 2017 kcse mock papers 2018 kcse mock papers pdf kcse mock papers pdf 2018 kcse mocks 2017 kcse mocks 2018 kcse music past papers kcse online past papers kcse papers 2015 kcse past papers kcse past papers - kcpe and answers - free mocks online - kcse answers past exams question papers - downloads | kcse papers and marking schemes | exams - kcse mathematics paper 1 questions and answers - kcse cre paper 1 questions and answers - knec past papers free downloads - kcse online registration - kcpe - kcse past papers - knec - knec portal - knec past papers for colleges - kasneb - past papers - kasneb past papers for colleges - cpa past papers - https://www.knec.ac.ke/ - www.knec-portal.ac.ke/ - knec portal: kcse results, online registration, kcse result slip. knec portal confirmation - knec portal kcse results - knec examiners portal - knec website kcse past papers - kcpe and answers - free mocks online - kcse answers past exams question papers - downloads | kcse papers and marking schemes | exams - kcse mathematics paper 1 questions and answers - kcse cre paper 1 questions and answers
kcse past papers 2007 kcse past papers 2009 kcse past papers 2010 kcse past papers 2011 kcse past papers 2011 pdf kcse past papers 2012 kcse past papers 2013 kcse past papers 2013 -knec kcse past papers 2014 kcse past papers 2014 pdf kcse past papers 2015 kcse past papers 2015 marking schemes kcse past papers 2015 pdf kcse past papers 2016 kcse past papers 2016 pdf kcse past papers 2017 kcse past papers 2017 pdf kcse past papers agriculture and answers kcse past papers arabic and answers kcse past papers art and design and answers kcse past papers biology kcse past papers building and construction and answers kcse past papers business studies and answers kcse past papers chemistry kcse past papers chemistry and answers kcse past papers chemistry pdf kcse past papers computer studies and answers kcse past papers cre and answers kcse past papers electricity and answers kcse past papers english and answers kcse past papers french and answers kcse past papers general science and answers kcse past papers geography and answers kcse past papers german and answers kcse past papers history and government and answers kcse past papers home science and answers kcse past papers hre and answers kcse past papers ire and answers kcse past papers kenya sign language and answers kcse past papers kiswahili and answers kcse past papers marking scheme kcse past papers maths kcse past papers metal work and answers kcse past papers music and answers kcse past papers pdf download kcse past papers physics and answers kcse past papers physics with answers kcse past papers power mechanics and answers kcse past papers with answers kcse past papers woodwork and answers kcse physics past papers kcse prediction 2017 kcse prediction 2018 kcse prediction 2018 pdf kcse prediction papers 2018 kcse prediction questions 2018 kcse prediction questions and answers kcse questions and answers kcse questions and answers. download free kcse past papers from knec. all marking schemes - questions and answers are sourced from knec. kcse revision kcse revision papers 2014 kcse revision | secondary school | text books | text book centre kcse trial 2017 kcse trial exams 2017 kenyaplex kcse past papers kenyaplex past papers for secondary kiswahili paper 3 questions and answers klb biology form 3 pdf klb cre form 1 klb cre form 3 knec ict past papers knec past papers for colleges knec past papers free download knec past papers pdf knec revision papers knec technical exams past papers kusoma.com past papers maths kcse 2017 mock past papers 2017 mock past papers with answers mokasa mock 2017 page navigation papacambridge computer science igcse past kcse papers past papers in kenya pre mocks 2018 pte knec past papers revision sample essays on betrayal in the city school biology notes school geography notes school physics notes school river and the source themes used in betrayal in the city xtremepapers igcse computer science z notes computer science igcse

No comments:
Post a Comment